Question
Question: Assertion: Cyclopentadienyl anion is aromatic in nature. Reason: Cyclopentadienyl anion has six \[...
Assertion: Cyclopentadienyl anion is aromatic in nature.
Reason: Cyclopentadienyl anion has six π electrons.
A.Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
B.Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion.
C.Assertion is incorrect but reason is correct.
D.Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
Solution
An aromatic compound follows Huckel’s Rule which states that a compound must have 4n+2 pi-electrons to attain aromaticity. A compound can be aromatic and non-benzenoid at the same time if it follows Huckel’s rule but does not have benzene structure or it can be aromatic and benzenoid if it follows Huckel’s rule and has benzene structure.
Complete step-by-step answer:
To be an aromatic compound or to attain aromaticity, a compound must fulfil these four conditions:
The molecule should be cyclic.
Every atom in the cyclic ring must be conjugated which provides the cyclic ring delocalized pi-electron system.
The compound must follow Huckel’s rule i.e. 4n+2 pi-electrons.
The molecule must be flat or planar as they possess large potential energy.
According to Huckel’s rule, all planar and aromatic compounds must have [4n+2] pi-electrons where n is an integer where n = 0, 1, 2, etc. Cyclopentadienyl anion has a planar ring structure with two pi bonds and four pi-electrons. The anion contributes two more electrons to the system which are in conjugation with the two double bonds and makes it a six-electron system. This now follows Huckel’s rule i.e. [4n+2] rule in which n=1 . Thus, it is an aromatic compound. Also, it is a non-benzenoid structure as it has only five carbon atoms in its structure.
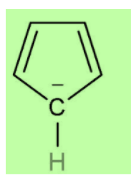
Cyclopentadienyl anion is aromatic in nature because it has six π electrons. Therefore, we can say that both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Hence the correct option is (A).
Note: If we look at cyclopentadienyl cation, we can see that it has only two double bonds in conjugation i.e. 4 pi-electrons only. As it does not follow Huckel’s rule ( 4n+2 pi-electrons), it is called an antiaromatic compound. Anti-aromatic compounds are cyclic, conjugated and have 4n pi-electrons and are flat too.
