Question
Question: Assertion-\[C{S_2}\] is linear whereas \({H_2}S\) is non-linear Reason-\(C\) in \(C{S_2}\) is \(sp...
Assertion-CS2 is linear whereas H2S is non-linear
Reason-C in CS2 is sp− hybridized whereas S in H2S is sp3− hybridized.
A.Both assertion and reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation for assertion.
B.Both assertion and reason are correct but the reason is not the correct explanation for assertion.
C.Assertion is correct but the reason is incorrect.
D.Assertion is incorrect but the reason is correct.
Solution
Orbital hybridisation (or hybridization) is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals (with different energies, shapes, etc., then the component atomic orbitals) suitable for the pairing of electrons to form chemical bonds in valence bond theory.
Complete answer:
CS2 molecule has linear geometry because the central atom carbon has sp− hybridization. It will use one
s and one p orbitals to form the hybrids, and the remaining p orbitals to form pi bonds with the two sulphur atoms. The molecular geometry will thus be linear.
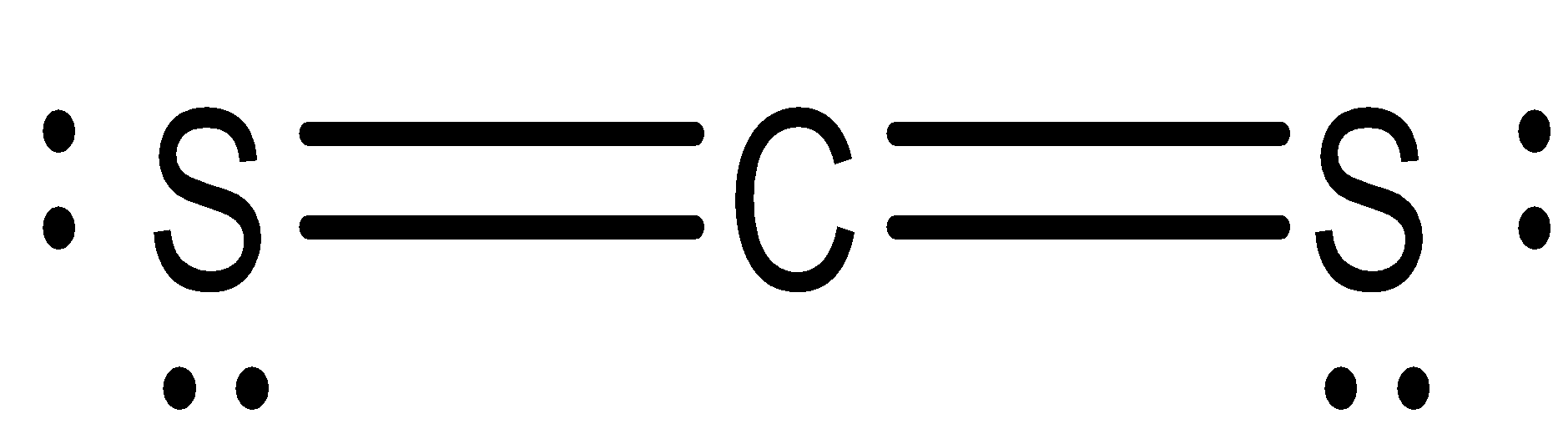
$C{S_2}$
H2S molecule has angular geometry because central atom sulfur has sp3 hybridization. In H2S, s is the main atom which has 2 lone pairs. These lone pairs cause repulsion and move the H−S bond away causing a non-linear shape Because it has 2 bonds and 2 unshared pairs in the central atoms it would be bent. In order to qualify as linear, the atom would only have two bonding regions occupied.
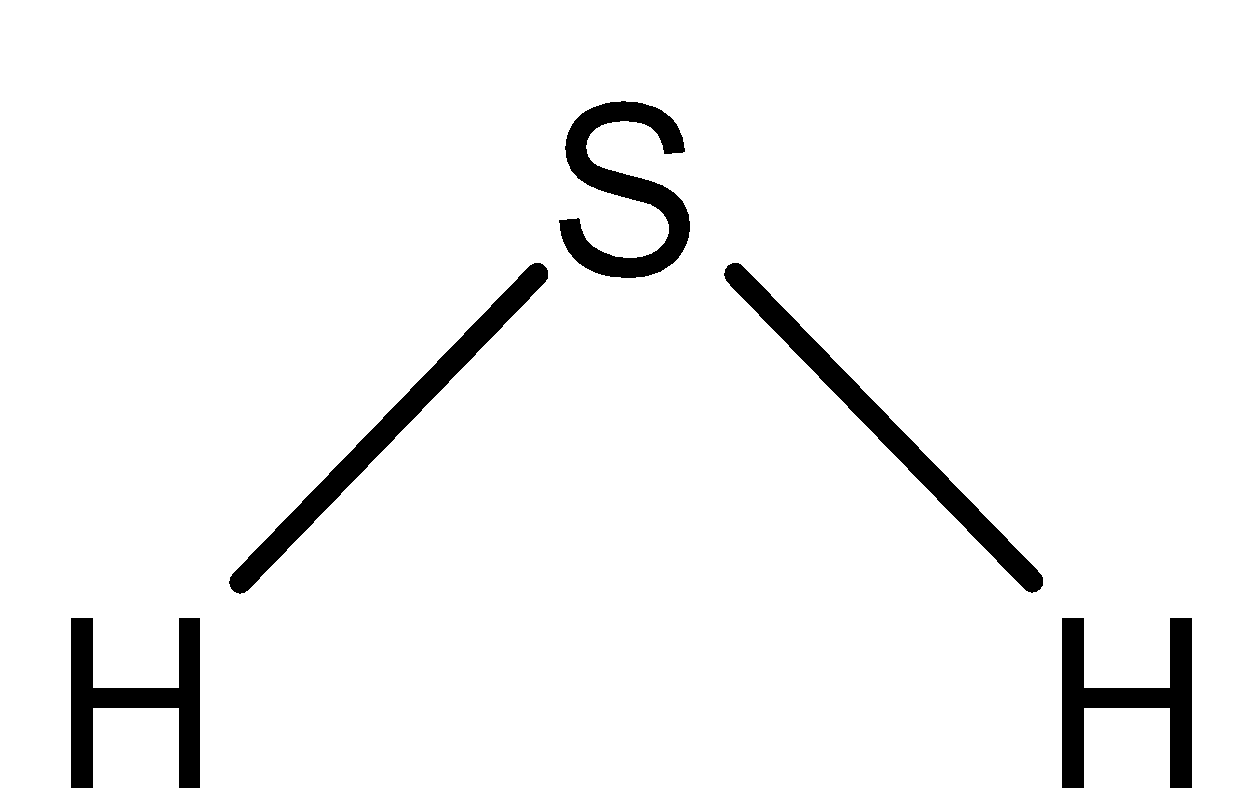
H2S
So, both assertion and reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation for assertion.
So, the correct answer is (A) Both assertion and reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation for assertion.
Note:
Sulfur atoms from the double bonds on both the sides of the Carbon atom in the linear form with the same charge and dipole strength. As the same molecules are present on both sides, it cancels out the charge due to its linearity, and the molecule becomes non-polar.
