Question
Question: Assertion \[C{H_3}CO{O^ - }\] (acetate ion) is more stable than \[{C_2}{H_5}{O^ - }\] (ethoxide io...
Assertion
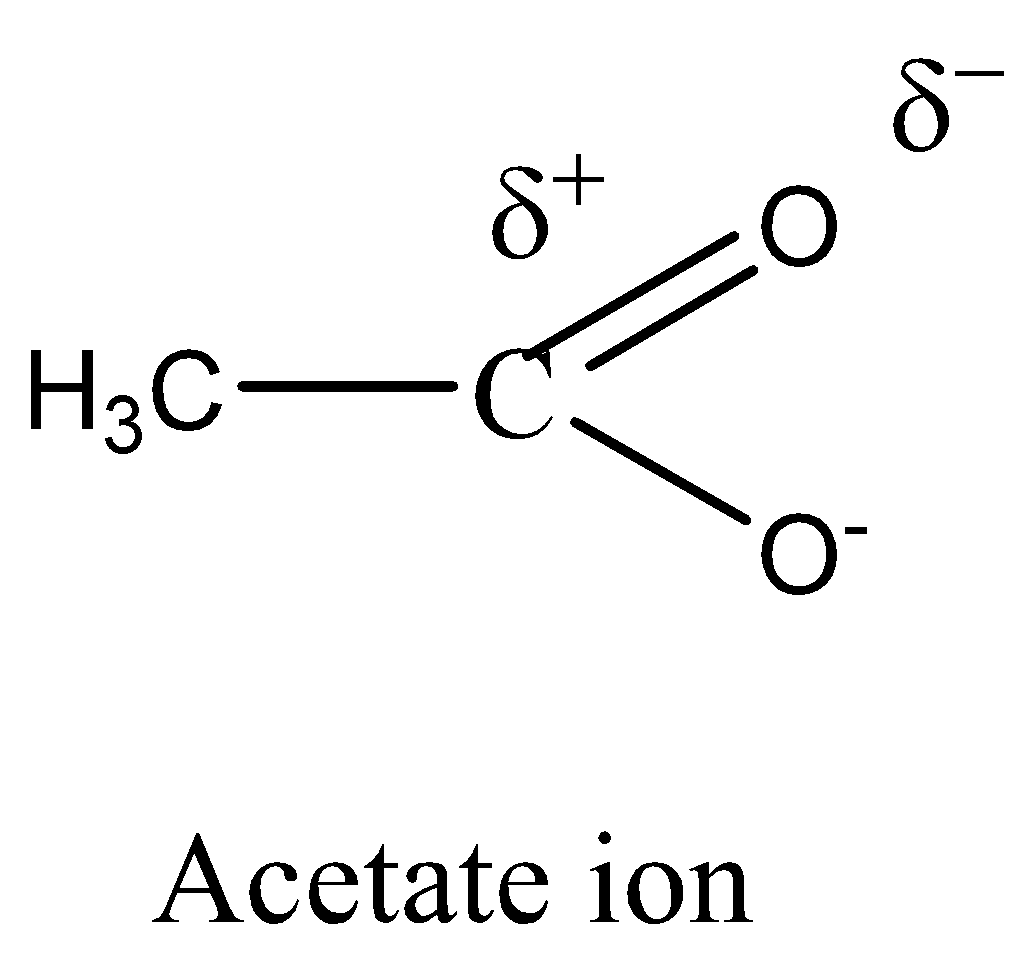
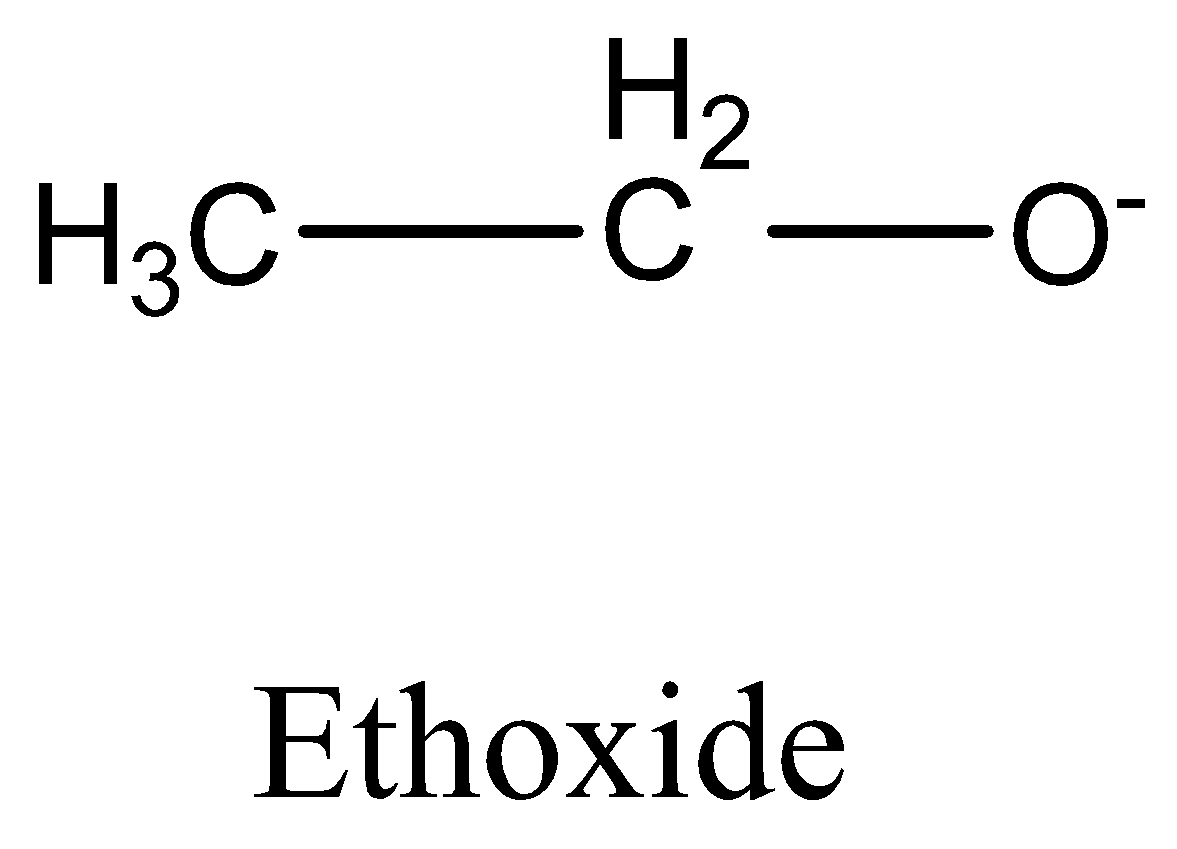
CH3COO− (acetate ion) is more stable than C2H5O− (ethoxide ion).
Reason
Electron delocalisation causes the negative charge in acetate to be shared equally by both oxygens. This type of resonance effect is not possible in ethoxide ion.
A.Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion
B.Both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion
C.Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect
D.Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect
Solution
We need to remember that acetate is an anion of monocarboxylic acid that formed from acetic acid carboxyl group by the removal of a proton. As a human metabolite and a metabolite of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, it has a function. It is an acetic acid conjugate base.
The ethoxide ion is a nucleophile that is almost "bare" It can attack the substrate better and is therefore a stronger nucleophile. The ethoxide ion is also a strong base, so the aldol condensation is a competing reaction in acetone.
Complete step by step answer:
We must need to remember that the CH3COO− is more stable than C2H5O− (acetate ion) (ethoxide ion) respectively. It is due to the delocalization of electrons. Resonance structures induce all oxygens to share the negative charge in acetate equally. As the +I inductive effect of C2H5O− makes it unstable, this resonance effect is not possible in ethoxide ions.
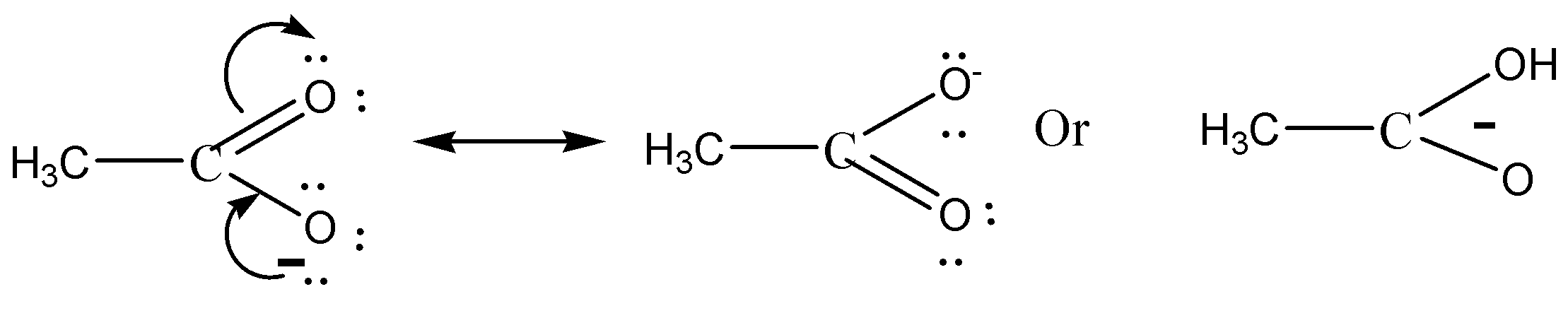
Both assertion and justification are also valid and reason is the right explanation for assertion.
In chemistry, the inductive effect is an effect on the transmission across a chain of atoms in a molecule of the unequal sharing of the bonding electron, leading to a permanent dipole in a bond.
Option A is the correct.
Note:
As we know that in chemistry, delocalized electrons are electrons which are not connected with a single atom or a covalent bond in a molecule, ion or solid metal. The word delocalization is general and in various fields it can have slightly different definitions. The resonance structure of a molecule depends on interaction between sigma and pi bond or two adjacent atoms.
