Question
Question: As given figure below, a voltmeter is connected across a bulb \(L\). If we decrease the resistance \...
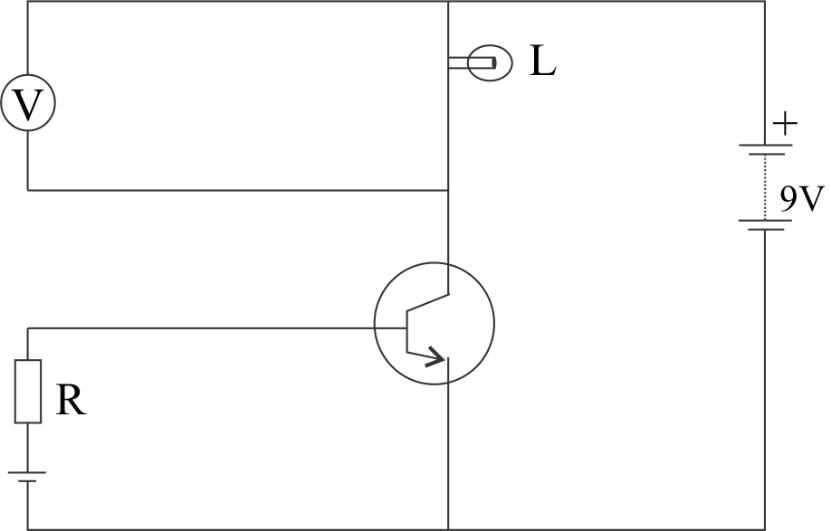
As given figure below, a voltmeter is connected across a bulb L. If we decrease the resistance R, how would it affect (i) the brightness of the bulb and (ii) the reading of the voltmeter? Justify your answer.
Solution
Given circuit is n-p-n junction transistor with CE configuration as shown in fig. The collector emitter circuit is reverse biased and the base-emitter circuit is forward biased. Brightness of bulb increases with increase in voltage across the bulb or decreases with decrease in voltage across the bulb. The voltmeter is connected parallel with the bulb so the effect on reading of voltmeter is the same as effect on brightness of bulb.
Complete step by step answer:
Given circuit is a n-p-n junction transistor with CE configuration as shown in fig. The collector emitter circuit is reverse biased and the base-emitter circuit is forward biased.
If resistance R is decreased forward biased in base-emitter circuit increases, due to which base current will decrease and emitter current will increase.
As collector current = emitter current – base current, collector current also increases.
When the collector current increases which flows through the bulb, voltage across the bulb also increases. Then the brightness of the bulb will increase on decreasing resistance R. Voltage meter shows the reading of potential across the bulb, then reading of voltage meter also increases.
Hence, on decreasing resistance R, both brightness of bulb and reading of voltmeter increases.
Note: Bulb is simple resistance which glows when current is passed through it. If we increase voltage across the bulb then current also increases like in case of simple resistor and brightness also increases. Voltmeter is always connected parallel to circuit because resistance of voltmeter is very large and in series it blocks the flow of current in circuit.
