Question
Question: Arrangement of nuclei in a normal dicot embryo sac is (a)3+3+2 (b)2+4+2 (c)3+2+3 (d)3+3+3...
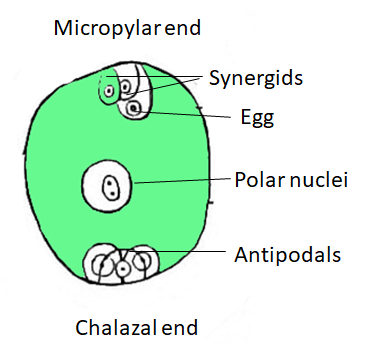
Arrangement of nuclei in a normal dicot embryo sac is
(a)3+3+2
(b)2+4+2
(c)3+2+3
(d)3+3+3
Solution
All the cells of the embryo sac are haploid except the central cell which becomes diploid because of the fusion of polar nuclei. The haploid sperm and haploid egg combine to make a diploid zygote, the method being called syngamy.
Complete answer:
The cells of an unfertilized ovule are 8 in number and arranged within the type of 3+2+3 (from top to bottom) i.e. 3 antipodal cells, 2 polar central cells, 2 synergids & 1 ovum. One sperm fertilizes the ovum and the other sperm combines with the 2 polar nuclei of the big central cell of the megagametophyte. The sperm and the two haploid polar nuclei of the big central cell of the megagametophyte organize a triploid nucleus (triple fusion). Some plants may form polyploid nuclei.
The two central cell maternal nuclei (polar nuclei) that contribute to the endosperm, arise by mitosis from a similar single meiotic product that gave rise to the egg. The maternal contribution to the genotype of the triploid endosperm is double that of the embryo.
Additional Information: Double fertilization is a complex fertilization mechanism of angiosperms (flowering plants). It involves the joining of a female embryo sac with two male gametes (sperm). It starts when a pollen grain sticks to the stigma of the carpel (the female reproductive structure of a flower). The pollen grain then grabs in moisture and starts to germinate, forming a pollen tube that stretches down toward the ovary through the style. The tip of the pollen tube then enters the ovary and penetrates through the micropyle opening within the ovule. The pollen tube proceeds to release the 2 sperm within the megagametophyte.
So, the correct answer is ‘3+2+3’.
Note: The female gametophyte is specifically termed a megagametophyte. It is additionally called the embryo sac in angiosperms. The large cell of the gametophyte will then become the endosperm, a nutrient-rich tissue that provides nourishment to the developing embryo. The ovary, surrounding the ovules, develops into the fruit, which protects the seeds and should function to disperse them.