Question
Question: Arrange the given set of compounds in order of increasing boiling point: \({\rm I}.\) \(1 - \)chlo...
Arrange the given set of compounds in order of increasing boiling point:
I. 1−chloropropane
II. isopropyl chloride
III. 1−chlorobutane
A. II<III<I
B. I<II<III
C. II<I<III
D. III<I<II
Solution
Boiling point of a substance is that temperature at which the substance converts from liquid to gaseous state. We can also say that at this temperature vapour pressure of the liquid is equal to the pressure surrounding the liquid. Boiling point of a substance varies with the surrounding environmental pressure.
Complete step by step answer: We know that boiling point is that temperature at which liquid changes to vapour state. In this question we have to arrange boiling points of 1−chloropropane, isopropyl chloride and 1−chlorobutane. Boiling point of hydrocarbons mainly depends on three factors, type of bonds, number of carbon atoms and branching of hydrocarbons.
More will be the strength of bond more will be the energy required. Ionic bond is the strongest bond followed by hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole interactions, and vander-wall forces. Boiling point will be highest for hydrocarbons containing ionic bonds followed by compounds containing hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole interactions, and vander-wall forces.
More will be the weight of the compound, more will be its boiling point. As the molecular weight of the compound increases its surface area also increases. Vander-wall forces are directly proportional to the surface area and due to increase in molecular weight surface area increases and vander-wall forces also increase. Which makes the bonding between molecules even stronger and more energy will be required to keep them away from each other (in vapour state distance between molecules is very large). 1−So, as the molecular weight increases boiling point also increases.
Boiling point depends on surface area as well. More will be the surface area and more will be the boiling point. As due to increase in surface area molecules will occupy large space and have more space to increase bonding because vander-wall forces are directly proportional to the surface area. Branched hydrocarbons occupy less space as compared to the compounds in which there is no branching (branching decreases surface area). This means more will be branching less will be the boiling point.
Structure of chloropropane is:
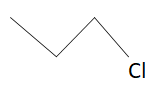
Let’s see other compounds as well.
Structure of isopropyl chloride is:
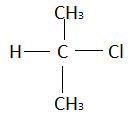
In 1−chloropropane there was no branching but in isopropyl chloride branching is present. This means the boiling point of isopropyl chloride will be less than that of 1−chloropropane (as explained above branching reduces boiling point).
Structure of 1−chlorobutane is:
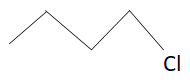
Like 1−chloropropane, 1−chlorobutane also has no branching. But molecular mass of 1−chlorobutane is more than that of 1−chloropropane as the number of carbons are more in 1−chlorobutane. As we know more is the molecular mass more is the boiling point. This means boiling point of 1−chlorobutane is more than that of 1−chloropropane (mass of 1−chloropropane is less than that of 1−chlorobutane).
This means boiling point of 1−chloropropane is more than that of isopropyl chloride but less than that of 1−chlorobutane. So, the correct order will be: II<I<III.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: In such types of questions first identify the compound with lowest molecular weight as less will be the mass less will be the boiling point. Then look for branching as more will be the branching less will be the boiling point.
