Question
Question: Arrange the following in the order of increasing value of the equilibrium constant for hydration, \(...
Arrange the following in the order of increasing value of the equilibrium constant for hydration, Khyd (smallest value first).
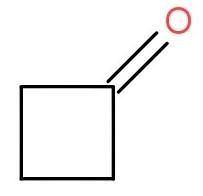
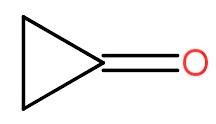
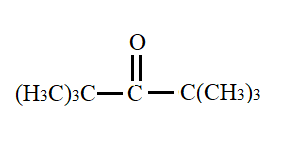
a.) 2 < 1 < 3
b.) 3 < 1 < 2
c.) 1 < 2 < 3
d.) 2 < 3 < 1
Solution
The answer is based on polarity of the CO bond. If the bond is more polar than it has a high value of equilibrium constant for hydration. The +I effect decreases the polarity of the bond while -I effect increases the polarity of the bond. The methyl groups are +I in nature.
Complete step by step answer:
We have studied the physical and chemical properties of aldehydes and ketones and from that we know that CO bond is polar in nature. This polarity of bond helps in its hydration. Thus, more polar is the bond, easier will be its hydration.
Now, we see the compound given to us in question and we will compare them.
The compounds given to us are cyclobutanone, cyclopropanone and 2,2,4,4- trimethylpentan-3-one.
Out of these, the third compound i.e., 2,2,4,4- trimethylpentan-3-one has a large +I effect due to presence of methyl group. This results in a decrease in its polarity. As a result, this compound shows least value for equilibrium constant for hydration.
Now, when we compare cyclobutanone and cyclopropenone then we see that cyclobutanone has more +I effect than cyclopropanone. Thus, out of these two; the cyclobutanone will be less polar.
So, by comparing all three we can conclude that cyclopropanone with lesser +I effect is the most polar and thus has a high value of equilibrium constant for hydration. The cyclobutanone comes after the cyclopropanone and at last the 2,2,4,4- trimethylpentan-3-one.
This can be seen diagrammatically as-
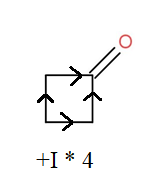
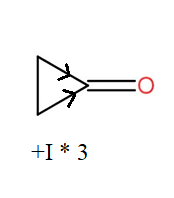
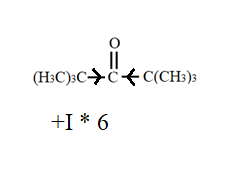
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: The CO bond is polar because there is electronegativity difference between the carbon atom and the oxygen atom. The Oxygen atom being more electronegative attracts the shared pair towards it. The methyl groups attached with carbon atoms in these compounds increase electron density at carbon. This results in a decrease in polarity of the bond.
If any electron withdrawing group is attached with this carbonyl carbon atom, then it would have increased the polarity of the bond and as a result, the order would have been reversed.
