Question
Question: Arrange ‘a’ to ‘f’ type H atoms in increasing acidic order. 
A. c<f<d<a<b<e
B. f<d<c<b<e<a
C. f<c<d<b<e<a
D. c<d<f<a<b<e
Solution
Hint : According to Bronsted theory of acids and bases, the substance or molecule which donates a proton is known as an acid and the anion ion formed after removal of proton is known as its conjugate base whereas if the substance accepts a proton, then it is known as a base and the cation formed after the accepting proton is termed as its conjugate acid.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
We know that the compounds which differ by only one proton are known as conjugate acid-base pairs. The use of conjugate acid-base pairs allows us to determine or predict the relative strength of acids and bases. According to the Bronsted Lowry concept, the stronger an acid, the weaker and more stable will be its conjugate base and conversely, the stronger a base, the weaker and more stable will be its conjugate acid.
Now, to check the relative acidic strength of marked H atoms, we need to compare the stability of its conjugate base. Let us look at the anion i.e., conjugate base formed in decreasing order of stability after removing each proton separately as follows:
Conjugate base formed after removal of H-(e):
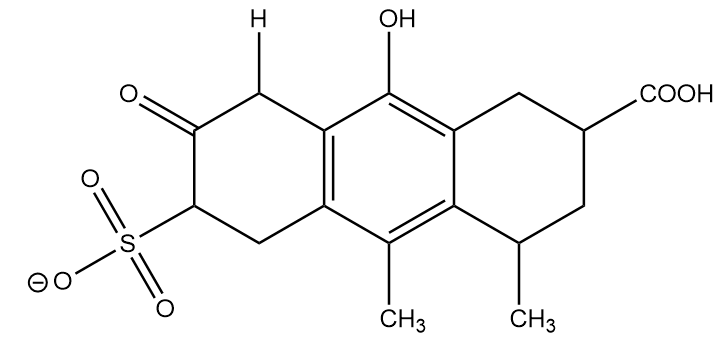
The conjugate base formed is the most stable anion because of resonance, it exists in three equivalent structures and greater the equivalent structures, more stable the molecule will be. Hence, the conjugate base formed at position (e) is most stable.
Conjugate base formed after removal of H-(b):
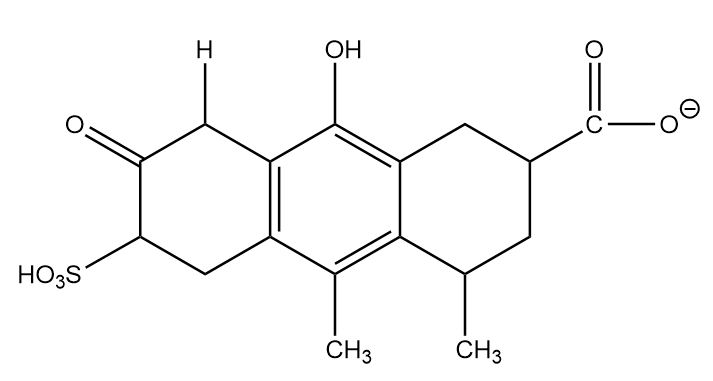
The conjugate base formed is the stable anion because of resonance, it exists in two equivalent structures and greater the equivalent structures, more stable the molecule will be. Hence, the conjugate base formed at position (b) will be placed at second position in stability decreasing order.
Conjugate base formed after removal of H-(a):
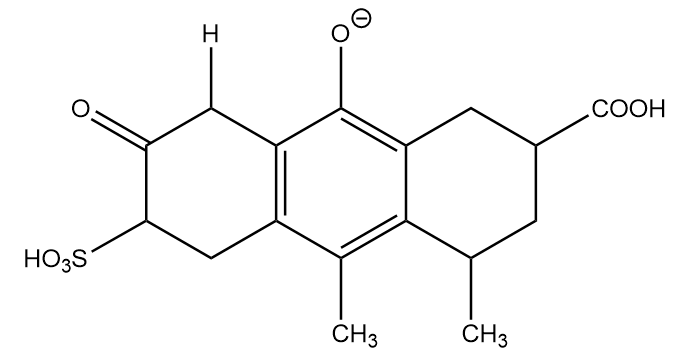
Although the phenoxide ion has a greater number of resonating structures, the negative charge in phenoxide ion resides on one electronegative element i.e., oxygen and the lesser electronegative elements i.e., carbon atoms. Hence, their contribution towards stabilization of phenoxide ions through resonance is less as compared to carboxylate ions. Hence, the conjugate base formed at position (a) will be placed at third position in stability decreasing order.
Conjugate base formed after removal of H-(f):
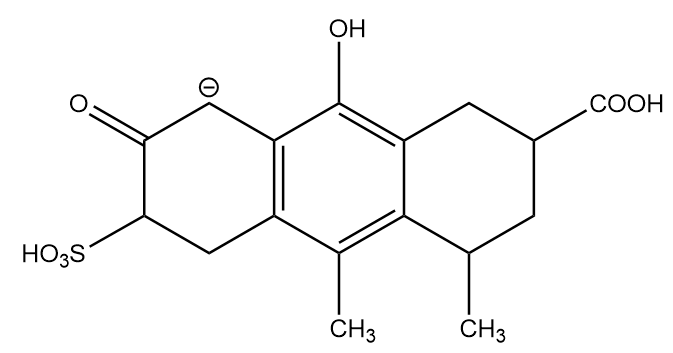
The conjugate base formed on removal of hydrogen at f position shows resonance and exists in two equivalent resonating structures. But due to the presence of only one oxygen atom, it is comparatively less stable. Hence, it is placed at fourth position in stability decreasing order.
Conjugate base formed after removal of H-(d):
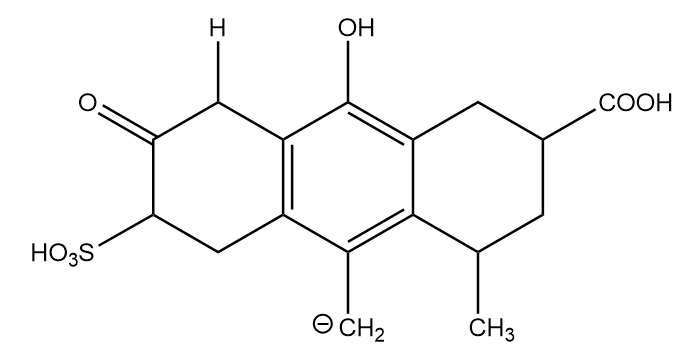
It is more stable than the conjugate base formed at position (c) just because of the presence of a benzene ring. Hence, it is placed at fifth position in stability decreasing order.
Conjugate base formed after removal of H-(c):
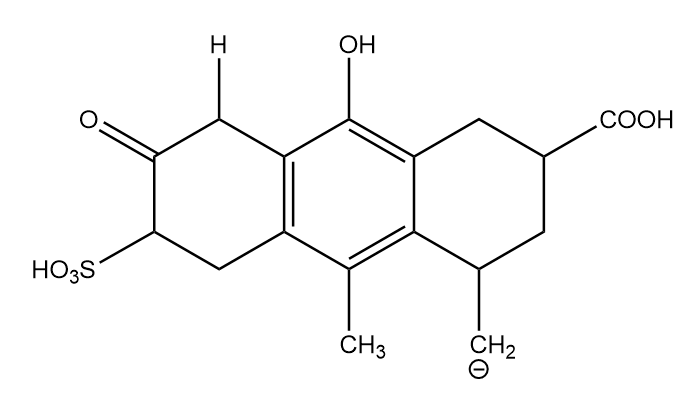
It is the least stable conjugate base because the negative charge is present on less electronegative elements and there is no resonance in the structure. Hence, it is placed at last position in stability decreasing order.
Therefore, the decreasing order of the stability of conjugate base formed at different positions is as follows:
e>b>a>f>d>c
So, the increasing acid order will be as follows:
c<d<f<a<b<e
Thus, option (d) is the correct answer.
Note :
Remember that a carbanion is a nucleophile whose stability and reactivity depends upon several factors like inductive effect i.e., the presence of −I group on the carbanion will stabilize the charge, the hybridization of charge bearing ion i.e., greater the s-character the more stable is the anion and the major factor is extent of conjugation of anion.
