Question
Question: Are these halides primary, Secondary or tertiary? How is this determined? A. 2-chlorobutane B. 2...
Are these halides primary, Secondary or tertiary? How is this determined?
A. 2-chlorobutane
B. 2-chloro-2-methylpropane
C. 1-chloro-2-butene
D. 1-chloro-2-methylpropane
E. 1-chloroadamantane
Solution
In primary halide, the halogen is attached to primary carbon. In secondary halide the halogen is attached to secondary carbon and in tertiary halide the halogen is attached to tertiary carbon atoms.
Complete answer:
- In the question it is asked to find the given compounds in the options are primary, secondary or tertiary halides.
- Coming to the given options. Option A, 2-chlorobutane.
- We should know the structure of 2-chlorobutane to find which type of halide it is.
- The structure of 2-chlorobutane is as follows.
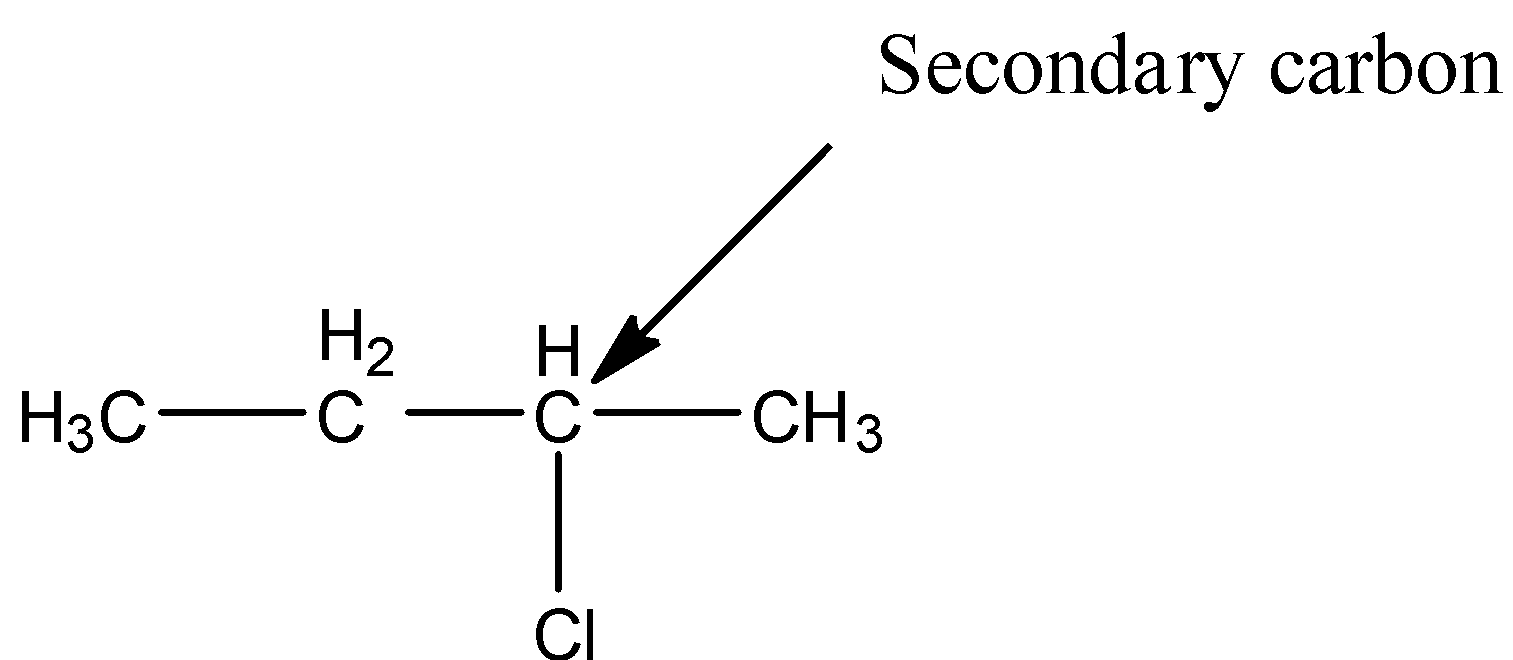
- In the above structure the chlorine is attached to secondary carbon then the halide is called secondary halide.
- Coming to option B, 2-chloro-2-methylpropane.
- The structure of 2-chloro-2-methylpropane is as follows.
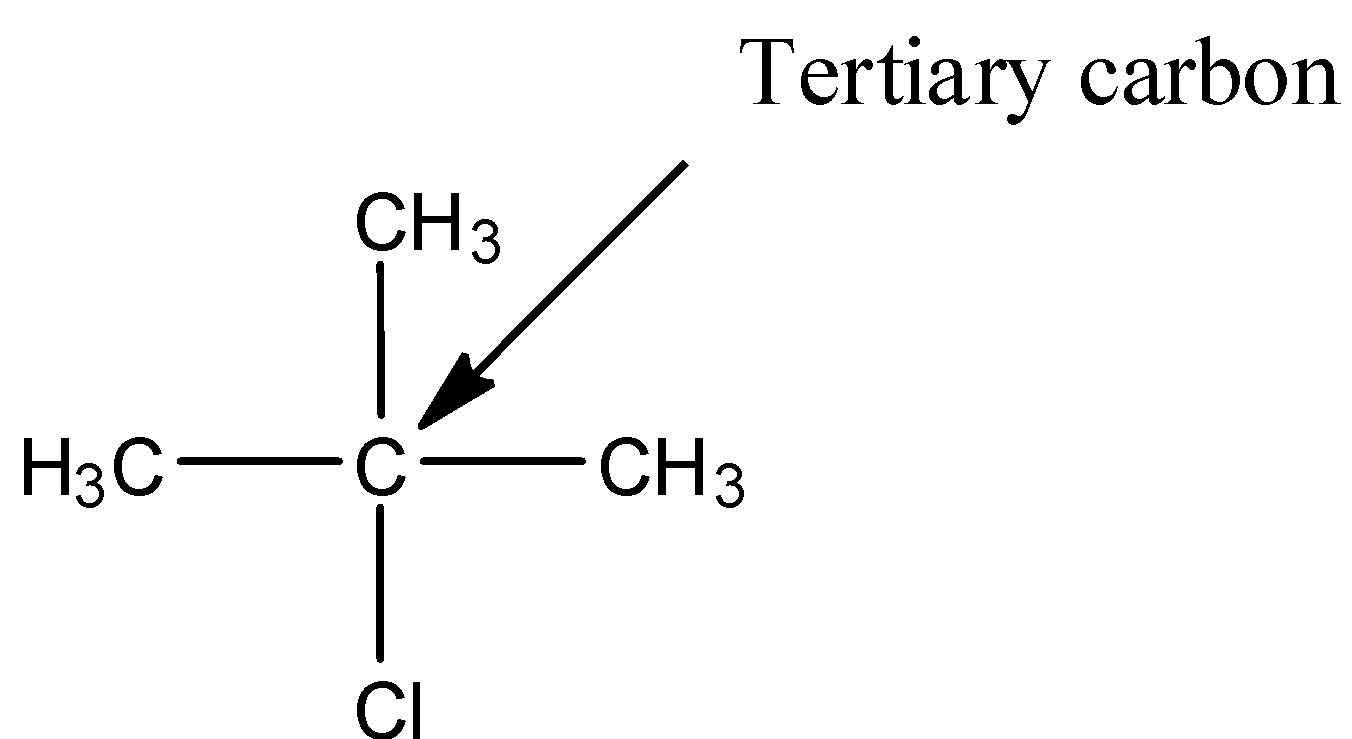
- In the above structure the chlorine is attached to tertiary carbon then the halide is called tertiary halide.
- Coming to option C, 1-chloro-2-butene.
- The structure of 1-chloro-2-butene is as follows.
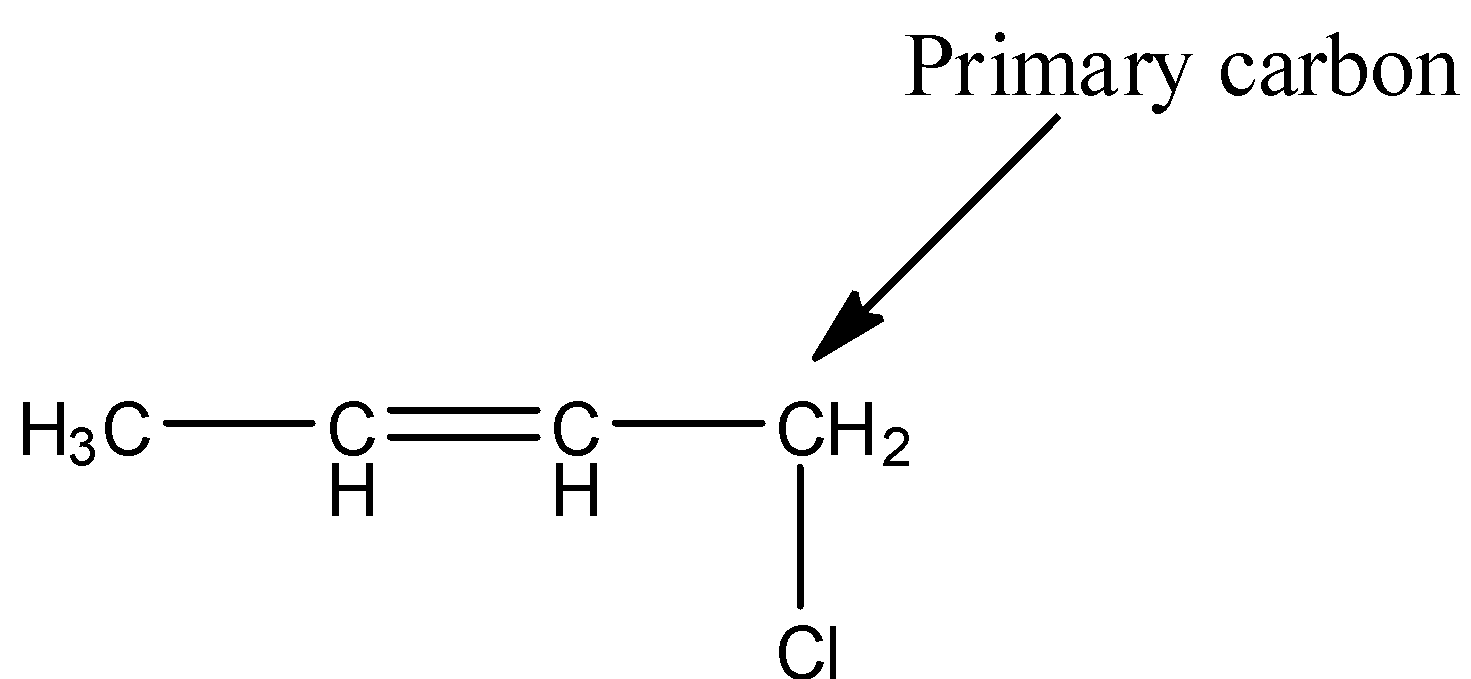
- In the above structure the chlorine is attached to primary carbon then the halide is called primary halide.
- Coming to the option D, 1-chloro-2-methylpropane.
- The structure of 1-chloro-2-methylpropane is as follows.
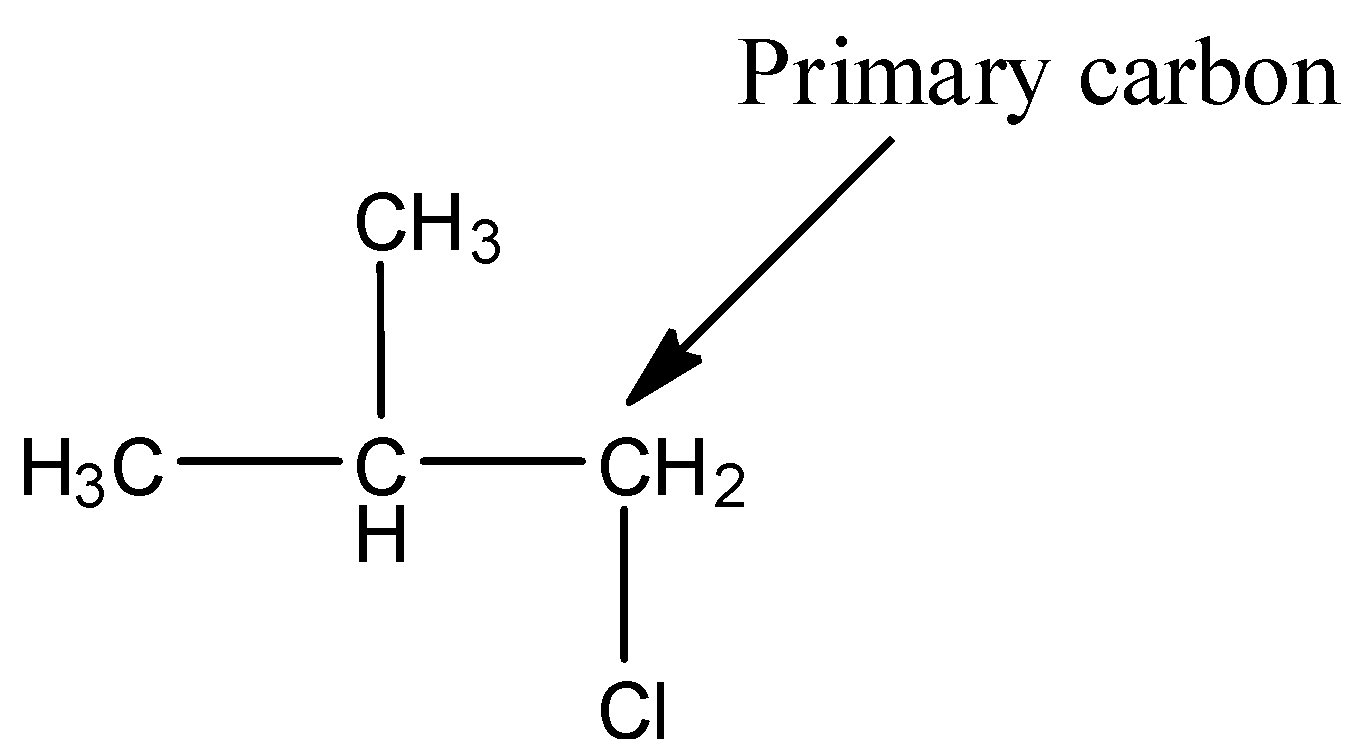
- In the above structure the chlorine is attached to primary carbon then the halide is called primary halide.
- Coming to option E, 1-chloroadamantane.
- The structure of 1-chloroadamantane is as follows.
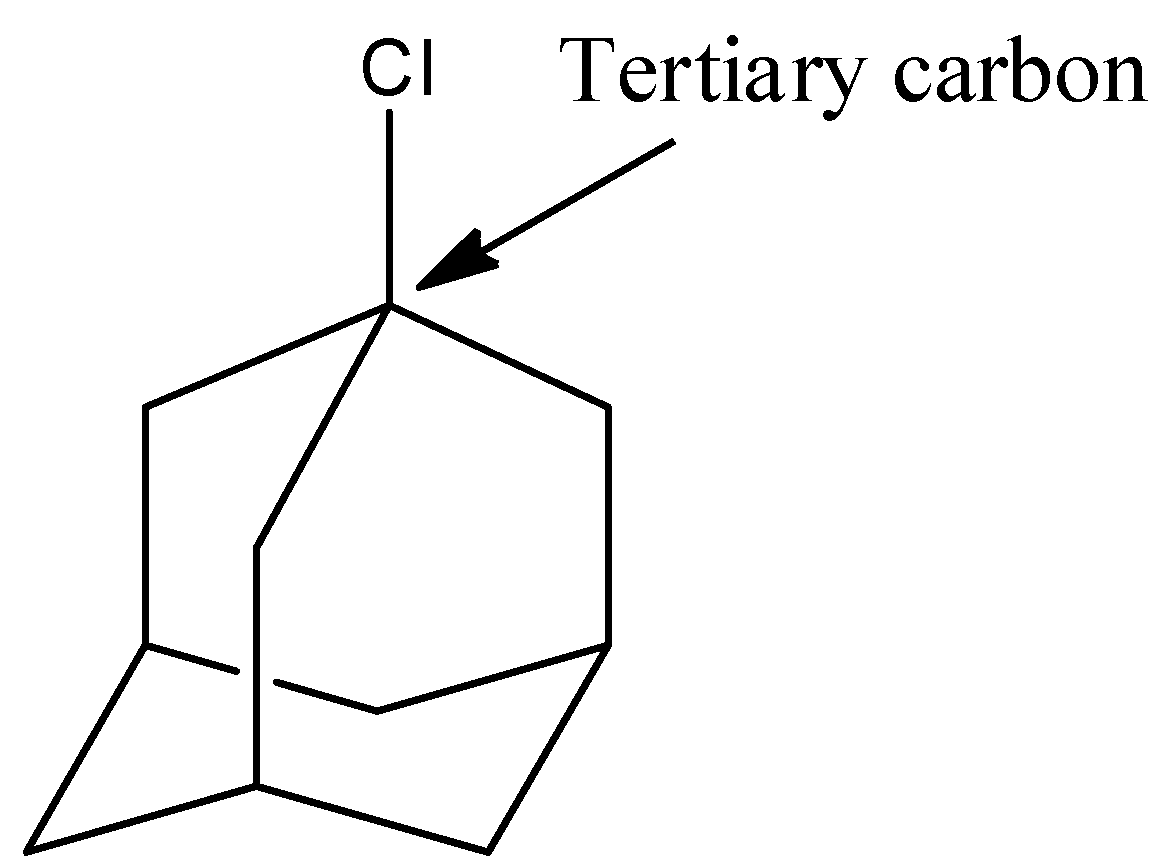
- In the above structure the chlorine is attached to tertiary carbon then the halide is called tertiary halide.
Note:
Only there is a chance to form three types of alkyl halides by organic compounds and they are primary, secondary and tertiary alkyl halides. Tertiary alkyl halides undergo SN1 reaction and form the respective derivatives easily.
