Question
Question: Antigenic determinants are A. Large and complex molecules that are different from those of an org...
Antigenic determinants are
A. Large and complex molecules that are different from those of an organism/host
B. Proteins or carbohydrates
C. Recognizable sites over antigens
D. Specific protein pathogen
Solution
An antigen is a substance when introduced into a body evokes an immune response to produce a specific antibody with which it reacts.
Types of antigens are as follows:
-Complete Antigen: These are substances that can induce antibody formation by themselves and can react specifically with these antibodies.
-Haptens: Haptens are substances unable to induce antibody formation on their own but can become immunogenic (capable of inducing antibodies) when covalently linked to proteins, called carrier proteins. These antibodies are produced not only against the hapten but also against the carrier protein
Complete answer:
An antigenic determinant in an antigen is “Epitope”. It is the smallest unit of antigenicity. Antigen possesses a number of these determinants. While the corresponding site of antibodies to which is corresponding to the epitope is called a paratope. This paratope binds to an epitope.
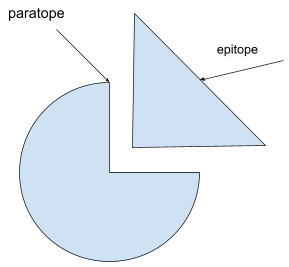
Additional information:
The exact basis of antigenicity is not clear but a number of factors have been implicated which make a substance antigenic. These factors are:
-Foreignness
-Size
-Chemical nature
-Susceptibility to tissue enzymes
-Antigenic specificity
Note: Antigen combines with its specific antibody in an observable manner and the reaction between antigen and antibody is specific. These antigen-antibody reactions when conducted in vitro are known as serological tests. These serological tests provide various diagnoses of infectious diseases and for non-infectious agents such as enzymes. These antigen-antibodies may lead to tissue injury in some hypersensitivity reactions and autoimmune diseases.
