Question
Question: Answer the following questions in two or three sentences: Explain the terms oxidation and reductio...
Answer the following questions in two or three sentences:
Explain the terms oxidation and reduction with examples. Explain the process Endothermic and exothermic with examples. Draw a diagram of Electrolysis of water and label oxygen and hydrogen.
Solution
Oxidation is removal of electrons in a chemical reaction and reduction is just opposite, addition of electrons. Endothermic is used for a chemical reaction when it absorbs heat energy for the reaction and exothermic releases heat energy during a chemical reaction. For electrolysis of water, electric current is passed through the acidic solution of water.
Complete step by step answer:
An oxidation reaction is a chemical reaction in which a molecule, atom or ion loses its electron. This in turn increases the oxidation number on the product. The name was used earlier for addition of oxygen in a chemical reaction. Conversely, a reduction reaction is a chemical reaction which leads to addition of electrons and then the oxidation number of the substance decreases. It was earlier related to addition of hydrogen in a chemical reaction. For example,
2Ag+H2S→Ag2S+H2
We have a silver reaction with hydrogen sulphide. Before the reaction, the silver atom has 0 as oxidation number and hydrogen has +1 as oxidation number. After the reaction, the oxidation number of silver increases to +1 and that of hydrogen decreases to 0. Thus according to the definition discussed above, silver oxidises and hydrogen got reduced. This reaction is also popularly known because many times, when in the laboratory, we are dealing with hydrogen sulphide, people are recommended to put out their silver ornaments because of the above reaction.
Any reaction which takes place with addition of heat to the products of the reaction is called endothermic reaction. Conversely, if heat is generated out of a chemical reaction then it is called the exothermic reaction. Most of the phase change reactions are either of these reactions. When we keep ice in an open normal room temperature, it starts to melt but this is an endothermic reaction because it absorbs heat energy from the ambient condition. Now phase change reaction starts at the surface where there will be more melting than solidification and thus the imbalance causes the melting to grow deeper ending with the whole volume of ice to melt. Similarly when water vapour condenses on the surface of a cold vessel straight from the refrigerator, the vapour loses heat to the vessel and forms a water molecule over the surface. So eventually, the vessel warms with time.
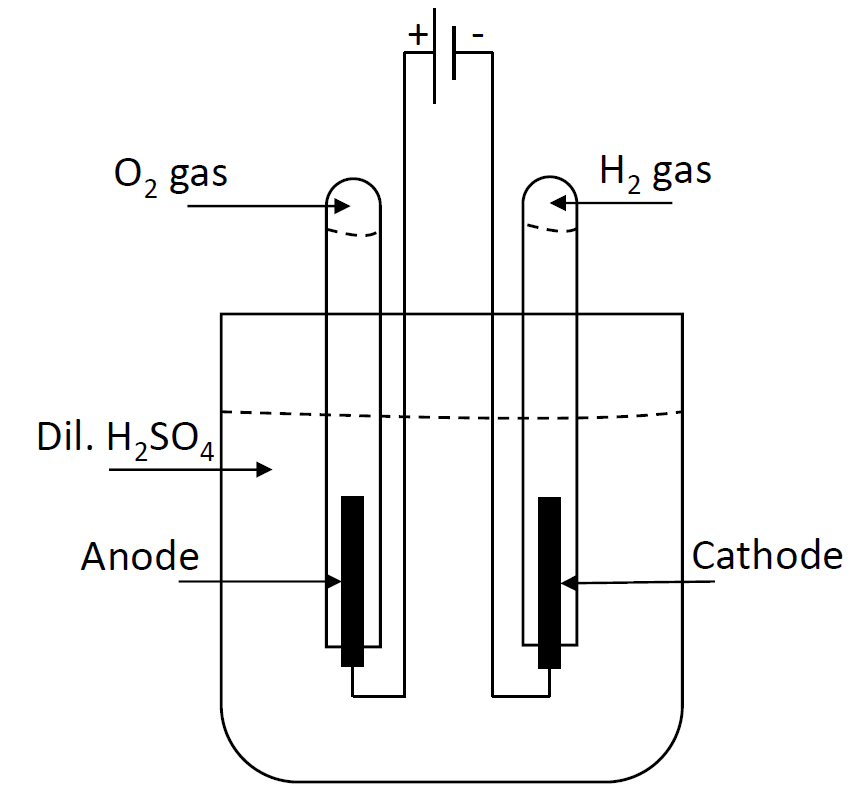
For electrolysis reactions to carry out, we need to pass electric current through acidified solutions of water. Dilute sulphuric acid is added to water which dissociates the water molecule to positive ions of hydrogen and negatives ions of hydroxide ions.
Reaction at anode (Positive electrode): All the negative ions generated in solution namely, SO42− and OH− are attracted to this electrode. Sulphate ion is stable in aqueous solution and thus not discharged. Whereas, the hydroxide ions discharges to produce oxygen gas at anode.
4OH−→2H2O+O2↑+4e−
Reaction at cathode (Negative electrode): All the positive ions generated in solution, namely the H+ ions are attracted to this electrode and after gaining electrons from the electrode, reduces to hydrogen. Thus we have hydrogen gas emission at the cathode rod.
2H++2e−→H2↑
Note: One nice natural application of endothermic reaction is the evaporation of sweat from our body. When sweat evaporates it absorbs heat energy from our skin and thus leaves our skin cooler than normal. We feel cooler when we are all sweat out and a wind blows over our skin. For oxidation and reduction reactions just note the oxidation number before and after the reaction to differentiate between each type of reaction.
