Question
Question: Answer the following questions: 1\. What is meant by chirality of compounds? Give an example. 2\...
Answer the following questions:
1. What is meant by chirality of compounds? Give an example.
2. Which one of the following compounds is more easily hydrolysed by KOH and why?
CH3CHClCH2CH3 or CH3CH2CH2Cl
3. Which one undergoes SN2 substitution reaction faster and why?
(Compounds are shown in below image)
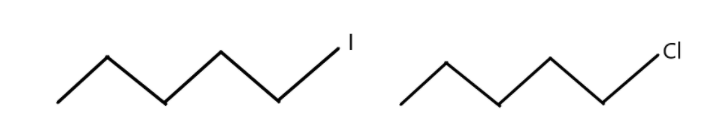
Solution
Chirality depends on the super impossibility of any compound. Hydrolysis is the addition of water molecules to a substance. SN2 Substitution reaction is a bi-molecular nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
1. In chemistry, a molecule or ion is called chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image by any combination of rotations and translations. This geometric property is called chirality. For example Butan-2-ol is a chiral molecule. This molecule exists in two stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other called enantiomers. The enantiomers have the same physical properties except that they have opposite optical activities. A chiral molecule or ion must have at least one chiral centre or stereo centre. When that centre coincides with an atom the substance is said to have point chirality.
2. Hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Hydrolysis of 2-chloro butane by KOH will result in the formation of secondary carbocation as an intermediate ad hydrolysis of chloropropane will result in the formation of primary carbocation. As secondary carbocation is more stable than primary carbocation due to inductive effect, hence hydrolysis of 2-chloro butane by KOH will be much easier.
3. The SN2 reaction is a nucleophilic substitution reaction which is a bi-molecular reaction. The rate determining step of this reaction depends on the interaction between the two species, namely the nucleophile and the organic compound. We know that as the size of Iodine is greater than chlorine because of more number of electrons in iodine. As the size of iodine is larger, it is a better leaving group than chlorine. Therefore, compounds with iodine will undergo SN2 substitution reaction faster than the compound with chlorine.
Note:
Chirality is when a molecule cannot be superimposed on its mirror image by any combination of rotations and translations. Hydrolysis is the addition of water molecules to a substance. Also secondary carbocation is more stable than primary carbocation. Also, the molecule with larger size is a better leaving group because of its larger size.
