Question
Question: Answer the following question. a. Deficiency of which vitamin causes night-blindness? b. Name th...
Answer the following question.
a. Deficiency of which vitamin causes night-blindness?
b. Name the base that is found in the nucleotide of RNA only.
c. Glucose on reaction with HI gives n-hexane. What does it suggest about the structure of glucose?
Solution
We all know that vitamins are the organic compounds which are required in small quantities for proper functioning of our body’s metabolism and RNA along with other macromolecules like lipids, carbohydrates and proteins are essential for any organism to survive.
Complete answer:
a. As we already know that vitamins are the organic compounds required in trace amounts by an organism to perform specific cellular functions. Vitamins are essential nutrients and they are not synthesised in our body, therefore we need to obtain these micronutrients from the diet. Majorly we have a total of thirteen vitamins including vitamin A, vitamin B1, vitamin B2, vitamin B3, vitamin B5, vitamin B6, vitamin B7, vitamin B9, vitamin B12, vitamin C, vitamin D, vitamin E and vitamin K. vitamins can be fat-soluble and water soluble.
Also, Night-blindness is the inability to see very well at night or in low light. It may be present from birth or caused by any injury to the eye or deficiency of nutritional products.
Let us discuss the vitamins now the first one is Vitamin A that involves Retinal which is a component of the visual pigments of rods and cone cells. These rods cells contain a pigment protein called rhodopsin which when exposed to light undergo some conformational changes and create signals which are carried to the brain. When light is absent, regeneration of rhodopsin takes place and if there is deficiency of vitamin A, it would not be possible and rods become incapable to respond to light causing night blindness.
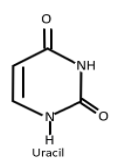
b. Now comes the RNA, the RNA world hypothesis proposed that it was actually the first life-forms on earth. It is that molecules play a critical role in the transfer of the genetic information stored in DNA into protein. Most RNA present in an organism is non-genetic and may be coding called mRNA or non-coding called tRNA, rRNA, snRNA etc. RNA consists of four nitrogenous bases named as Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Uracil. Uracil is the only base which is found in RNA and not in DNA while the other three are common in DNA along with Thymine. Thus, we can name the base which is Uracil found in the nucleotide of RNA only.
c. Finally the reaction between Glucose and HI: As we know that Hydrogen iodide is a strong reducing agent, hence it will reduce the alcohols and aldehyde groups in glucose molecule into a straight chain of carbons and we can understand this with the chemical reaction:
CHO−(CHOH)4−CH2OHHIΔCH3−CH2−CH2−CH2−CH2−CH3
Note:
Students may get confused in Thiamine and Thymine. Thiamine is the vitamin B1 which is a water soluble vitamin and its deficiency can result in Beri-Beri syndrome which is found in areas where polished rice is the major component of diet and Thymine is one of the four nitrogenous bases found in DNA.
