Question
Question: Animals that have milk-producing glands to nourish their young ones belong to which class of Animali...
Animals that have milk-producing glands to nourish their young ones belong to which class of Animalia?
Solution
A mammary gland is an exocrine gland that produces milk to feed newborn offspring in humans and other mammals. Mammalian species are named after the Latin term mamma, which means "breast."
Complete answer:
Lactation, the production of adequate milk for feeding, occurs only in phenotypic females who have gestated within the last several months or years in most mammals. Mammals are a group of animals that have a placenta, give birth to offspring, and feed them milk produced by the mammary glands.
The mammary glands are found in organs like the breasts of primates like humans and chimps, the udder of ruminants like cows, goats, and deer, and the dugs of other animals like dogs and cats. Prototherians, metatherians, and eutherians are the three groups of mammals. Both males and females have functioning mammary glands in prototherians, however, their mammary glands lack nipples. These mammary glands are sebaceous glands that have been modified.
Only females have functional mammary glands in metatherians and eutherians. Breasts or udders are the terms for their mammary glands. Pairs of mammary glands form a single mass in udders, with more than one nipple dangling from it. Cows and buffalo, for example, have a single udder with four teats, whereas sheep and goats have two teats extending from the udder. These mammary glands are sweat glands that have been modified.
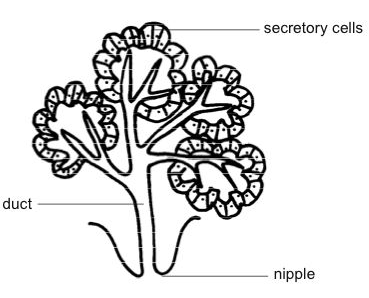
Note: Hormones control the function of the mammary gland. Increased oestrogen levels drive the growth of glandular tissue in the female breast throughout adolescence. Estrogen also causes adipose tissue to accumulate in the breast, causing it to grow in size. Progesterone aids in the formation of the duct system.
