Question
Question: Aniline reacts with excess \[{\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_2}/{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}\] to give the major p...
Aniline reacts with excess Br2/H2O to give the major product:
A.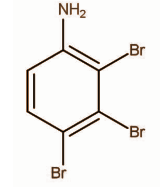
B.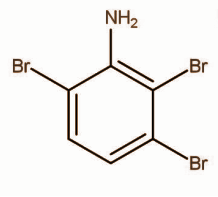
C.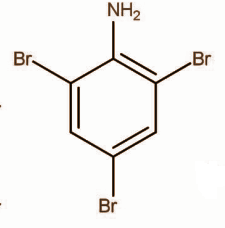
D.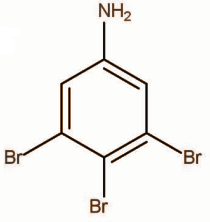
Solution
The NH2group is a very good activating group. It increases the electron density at ortho and para position. Due to strong activation of benzene ring poly substitution occurs.
Complete step by step solution:
Halogenation of phenols or aniline occurs via electrophilic substitution reaction. In general to produce electrophile a Lewis acid is required. In the above reaction water acts as a Lewis acid which gives rise to the required electrophile. Water is a highly polar solvent hence it supports the poly substituted. However in the presence of low polar solvents such as chloroform and carbon tetrachloride only mono substituted product forms, ortho and para substituted products are formed.
In phenol and aniline hydroxide and amine respectively are activating groups in such cases Lewis acid are not required. Halogen which generally exists as a diatomic molecule breaks heterolytically and electrophile is generated. The reaction of aniline with bromine in the presence of water occurs as:
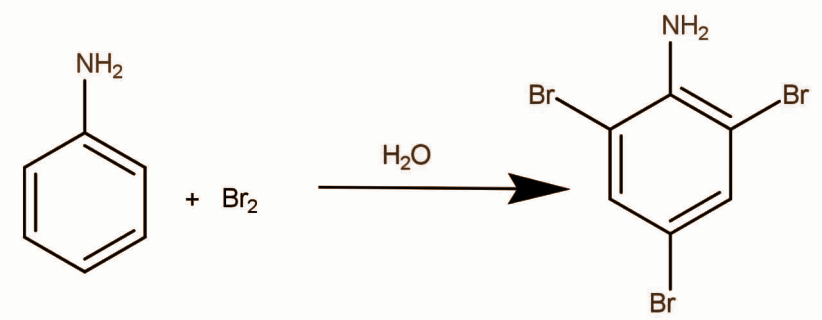
White precipitate of 2,4,6-tribromoaniline is formed.
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note: The groups like NH2 and OH show mesomeric effect. Mesomeric effect is the resonance shown by the presence of a functional group. Due to resonance these groups donate electron density to the benzene ring. The electron density increases on ortho and para position on the benzene ring. Ortho position is the position next to the functional group attached to the benzene ring. Meta position is the second position corresponding to the group attached to the functional group. Para position is the third position with respect to the functional group attached. There are 2 ortho and 2 Meta positions and only one para position.
