Question
Question: An unknown alkyl halide \(\left( A \right)\) reacts with an alcoholic KOH to produce a hydrocarbon \...
An unknown alkyl halide (A) reacts with an alcoholic KOH to produce a hydrocarbon C3H8 . Ozonolysis of the hydrocarbon forms 1 mole of propionaldehyde and 1 mole of formaldehyde. Suggest which of the following organic structures is the correct structure of the above alkyl halide (A) .
a) CH3CH2CH2CH2Br
b) CH3CH(Br)CH(Br)CH3
c) CH3CH2CH(Br)CH3
d) BrCH2CH2CH2Br
Solution
The process takes place in two parts; first the dehydrohalogenation takes place and in the next process ozonolysis . Dehydrohalogenation is the removal of halogen and water molecules from alkane. Ozonolysis takes place when alkenes, alkynes or azo compounds are cleaved by ozone.
Complete answer:
-Products that are formed during ozonolysis are propionaldehyde and formaldehyde.
-The structure of propionaldehyde and formaldehyde is as follows:
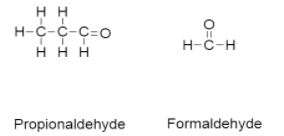
-Ozonolysis takes place only when the unsaturated bond of alkenes, alkynes and azo compounds are cleaved by ozon.
-This denotes that there was a carbon-carbon double bond between propionaldehyde and formaldehyde.
-So the possible structure before ozonolysis are as follows:
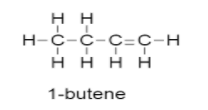
-So from this structure we can say that the unknown alkyl halide A may be 1−bromobutane .
Now assuming 1−bromobutane as the unknown alkyl halide we will carry out the reaction as follows:
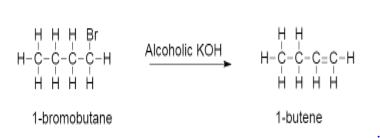
-In this process, HBr gets replaced by a double bond.
-The removal of halogen and β− hydrogen from an alkane is the process of dehydrohalogenation.
-This β− hydrogen is removed from β− carbon atom which is adjacent to the halogen atom.
-Also during this process there is removal of water molecules.
-Later on when this 1−butene undergoes ozonolysis it gives propionaldehyde and formaldehyde
-The reaction is given as follows:
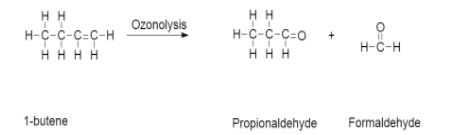
-From all the above reaction we can say that the unknown alkyl halide (A) is CH3CH2CH2CH2Br.
So the correct answer is option (a) CH3CH2CH2CH2Br
Note:
Ozonolysis of alkenes gives us aldehyde, ketones, alcohol or carboxylic acids.It is a type of redox reaction. It also helps to detect the location of double bond or triple bond present in alkenes and alkynes respectively.
