Question
Question: An organic compound (E) (\({C_5}{H_8}\) ) on hydrogenation gives a compound (F) (\({C_5}{H_{12}}\))....
An organic compound (E) (C5H8 ) on hydrogenation gives a compound (F) (C5H12). Compound (E) on ozonolysis gives formaldehyde and 2-keto propanal. Deduce the structure of compound (E).
A. cyclopentene
B. 1,4- pentadiene
C. 1,3- pentadiene
D. 2 methyl- 1,3- butadiene
Solution
Hydrogenation refers to the treatment of substances with molecular hydrogen (H2 ), adding pairs of hydrogen atoms to compounds (generally unsaturated compounds). Ozonolysis is an organic reaction where the unsaturated bonds of alkenes, alkynes, or azo compounds are cleaved with the help of ozone.
Complete step by step answer:
The process of hydrogenation is the simple addition of hydrogen atoms in a molecule and usually requires a catalyst for the reaction to occur under normal conditions of temperature and pressure. According to the given details, the reactions are as follows:
C5H8(E)H2C5H12(F)
C5H8(E)O3HCHO+CH3−C(=O)−CHO
(Formaldehyde) (2-keto propanal)
From the above reactions, it is clear that the molecule (E) has a two double bond system (diene system) as during the ozonolysis, the product formation takes place in the ratio of carbon atoms of 1:3:1. If it would have been a triple bond, the process of ozonolysis, if possible, would have been in the ratio of 2:3 . As we can see that there is a formation of 2-keto propanal, we can deduce the structure of diene (E) to be:
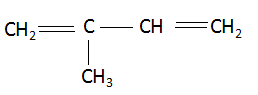
The name of the compound (E) is 2 methyl- 1,3- butadiene.
The overall reaction is as follows:
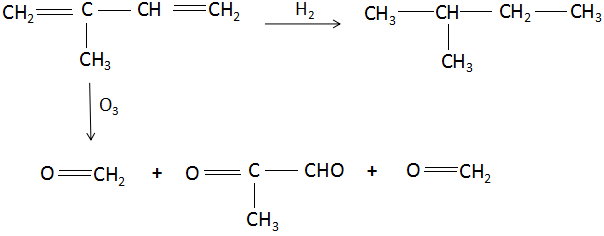
Thus, the correct option is: D. 2 methyl- 1,3- butadiene .
Note:
Alkenes can be oxidized with ozone to form alcohols, aldehydes or ketones, or carboxylic acids. Alkenes have a wide variety of reactions. It can undergo both oxidation as well as reduction. Hydrogenation is a reduction process and alkenes can undergo hydrogenation in the presence of a suitable catalyst which increases the surface area for the reduction of the alkene.
