Question
Question: An organic compound \({{C}_{3}}{{H}_{9}}N\) (A) when treated with nitrous acid, gave an alcohol and ...
An organic compound C3H9N (A) when treated with nitrous acid, gave an alcohol and N2 gas was evolved. (A) on warming with CHCl3 and caustic potash gave (C) which on reduction gave isopropylmethylamine. Predict the structure of (A).
[A] CH3CH2NHCH3
[B] CH3NCH3CH3
[C] CH3CH2CH2NH2
[D] (CH3)2CHNH2
Solution
To solve this, remember that primary amine react with acids to give alcohol. Identify the primary amines from the given option. Remember that the product obtained is isopropylmethylamine. So, the starting product must be an iso-amine and not n-amine.
Complete answer:
Here first of all we can see that (A) upon reaction with an acid gives an alcohol. We know that only a primary amine upon reaction with an acid gives us alcohol.
So, we can surely say that A is a primary amine. We know that primary amines are the amines having only one carbon attached to the nitrogen atom.
Also, it is given that the amine A on warming with chloroform and potassium hydroxide reduces to isopropylmethylamine.
We know that the structure of isopropylmethylamine is (CH3)2CHNHCH3
Now let us see the given options and find out the primary amine among them.
In the first option we have CH3CH2NHCH3 which is a secondary amine.
Then we have CH3NCH3CH3 which is a tertiary amine.
Next we have CH3CH2CH2NH2 which is a primary amine and the last option (CH3)2CHNH2 is also a primary amine.
Among these two, CH3CH2CH2NH2 is propylamine and (CH3)2CHNH2 is isopropyl amine. So, either of them can be the correct answer.
But upon reduction, we obtain isopropylmethylamine so the correct answer should be the isopropyl amine and not n-propylamine.
We can write the reaction as-
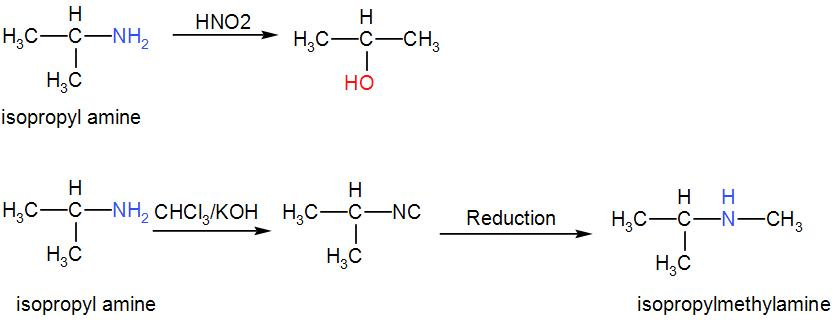
We can understand from the above discussion that the correct answer is option [D](CH3)2CHNH2.
Note:
Just like we’ve seen in the above discussion that primary amines give us alcohol with acid, similarly it also gives us a diazonium salt which forms alcohols on addition of water but secondary amines have one hydrogen atom attached on them therefore, they cannot complete the diazotization reaction and give us a yellow oily nitrosamine product. Three degree amines have no hydrogen atoms attached to them thus they undergo simple acid- base reactions and give us soluble salts.
