Question
Question: An organic acid (X) has the molecular formula \({{{C}}_{{8}}}{{{H}}_{{{10}}}}{{{O}}_{{2}}}\). (X) on...
An organic acid (X) has the molecular formula C8H10O2. (X) on heating with NH3form (Y) which on treatment with alkaline Br2forms. (Z) on treatment with HNO2followed by heating with H2SO4 gives 2,4−dimethyl−2−pentane. How many different acids (X) can give the indicated final product?
Solution
We draw the structure of eight carbon chains and such two oxygen functional groups which on reacting with ammonia gives amide as the next reaction is Hoffman bromamide reaction which acts on amide functional groups.
Complete step by step answer:
STEP 1 Since the final product have 7 carbon that means 1 carbon with 2oxygen can only form an ester or acid. Since we need only one carbon extra so it can be carboxylic acid only not ester as ester requires minimum 2 carbon. In this step nucleophilic attack of ammonia happens to form amide.
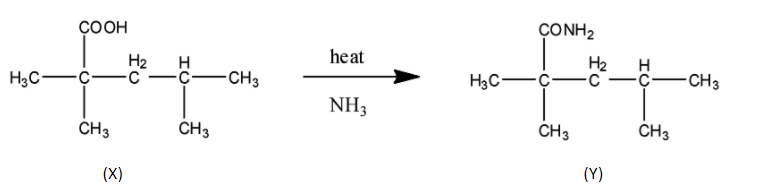
STEP 2 Next step is the reaction with alkaline Br2 which means KOH/NaOH+Br2 which is a name reaction called Hoffmann bromamide. In this reaction the amide group is converted to the amine group.
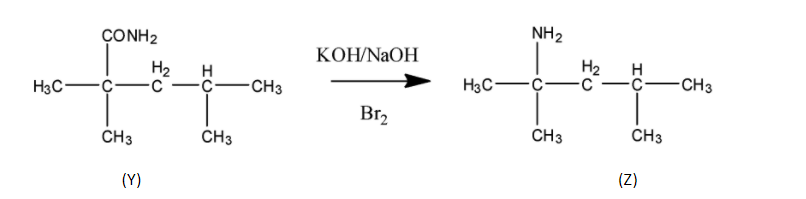
STEP 3 In this step HNO2 reacts with (Z) . This reaction is called diazotization in which the attacking nucleophile is NO+ which in presence of water form oxime and finally diazonium salt. So the product form in this step is a diazonium salt.
STEP 4 In this step ${{{H}}_{{2}}}{{S}}{{{O}}_{{4}}}$ is in aqueous state where water ions are present. Since ${{{N}}_{{2}}}^{{ + }}$ is a strong leaving group the water present in the solution attacks there and is replaced as hydroxide. After alcohol is formed due to heating the elimination of alcohol group occurs and alkene is formed. 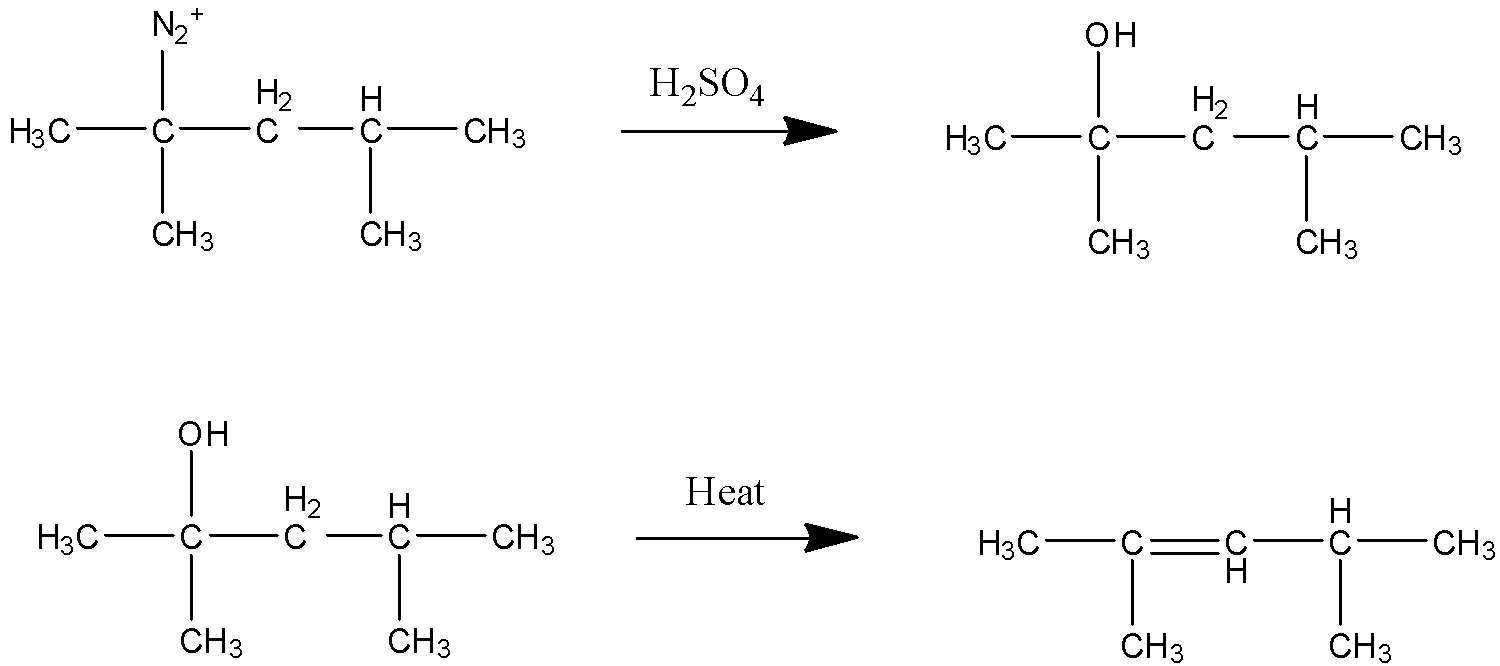 So the product (X) is given above **Additional information:** The diazotization reaction is a very important reaction. Since halo-benzenes are difficult to convert as they are a bad leaving group when attached directly to phenyl rings. So diazotization is the best reaction to convert those as good leaving groups and make different ranges of products. **Note:** The carbonyl group of acid is electrophilic in nature and ammonia is basic so it attacks on the carbonyl group and when the lone pair reverses from the oxygen the ${{ - OH}}$ group leaves and amide is formed by addition on ${{ - N}}{{{H}}_{{2}}}$.