Question
Question: An optically active hydrocarbon \(X\) has molecular formula \({C_6}{H_{12}}\) , \(X\) on catalytic h...
An optically active hydrocarbon X has molecular formula C6H12 , X on catalytic hydrogenation gives optically inactive C6H14 , X could be:
A.3−methyl−1−pentene
B.3−methyl−2−pentene
C.4−methyl−2−pentene
D.4−ethyl−1−butene
Solution
In this first we will find out whether the given molecular formula of hydrocarbon is an alkane, alkene or alkyne.Next we will see the catalytic hydrogenation of optically active hydrocarbon. Then accordingly we will see what is X .
Complete step by step answer:
The molecular formula of the optically active hydrocarbon: C6H12
This molecular formula is the same as that of alkenes, that is: CnH2n.
So, from this we can say that the above formula of the hydrocarbon is of an alkene.
We got to know that this is an alkene, so we have to assume some of the possible structures for it that is optically active.
Before this we will see, what do you mean by optically active and optically inactive:
Optically active means that they are non super imposable mirror images of each other, are asymmetric and can rotate plane polarized light means it has chiral carbon atoms.
Optically inactive compound means that it does not rotate along the plane polarized light, does not have any chiral carbon atoms.
Possible Optically active structure of hydrocarbon with molecular formula C6H12 is:
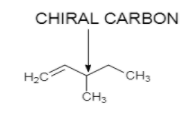
On catalytic hydrogenation, in the presence of H2/Pd it gives optically inactive compound with
molecular formula C6H12 :
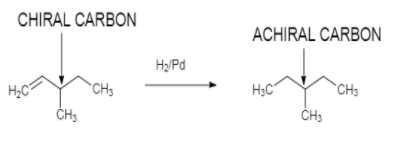
So from this we can assume that an optical active hydrocarbon X with molecular formula C6H12 is 3−methyl−1−pentene.
So, the correct answer is option A: 3−methyl−1−pentene.
Note:
The compound that is optically active, that can rotate along the plane polarized light are called enantiomers. Enantiomers are of two types: racemic mixture(enantiomers in equal ratio),R,S configurations.
