Question
Question: An optically active amine (A) is subjected to exhaustive methylation and Hofmann elimination to yiel...
An optically active amine (A) is subjected to exhaustive methylation and Hofmann elimination to yield an alkene (B). (B) on ozonolysis gives an equimolar mixture of formaldehyde and butanal. Deduce the structural of (A) and (B). Is there any structural isomer (A), if yes draw its structure?
Solution
In the above question, we have to determine the structure of A and B and we have to check if there is any structural isomer of A. Here, since the end products are given we should try to solve these questions backwardly. In short, first we have to see which product results in formation of formaldehyde and butanal and then we can proceed further. The first reaction results in formation of alkene and the second forms aldehyde.
Complete step-by-step answer: Ozonolysis is a process which takes place in unsaturated bonds of alkene or alkyne where the bond is replaced by oxygen atom.
In the above question, formaldehyde and butanal are formed, so we can replace the oxygen atom present in both the molecules by unsaturated carbon-carbon bond which indicates that the resultant reactant was pent-1-ene.
The reaction involving the above reaction is:

Pent-1-ene is formed by exhaustive methylation and Hoffmann elimination of A.
Since, in exhaustive methylation CH3 group is added in place of hydrogen atom in NH3 to makes nitrogen more electropositive and then Hofmann elimination takes place. It states that the less substituted alkene is the major product. Hence, the product formed is
The reaction involving the above reaction is:
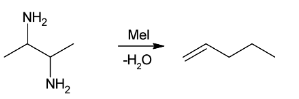
Overall reaction can be illustrated as:
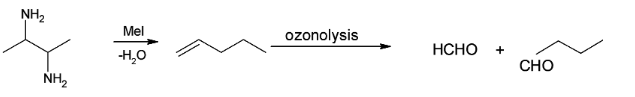
There is no structural isomer of A.
Note: Formaldehyde is a colourless and strong smelling gas which is used in building and household products.
Butanal is used in the manufacture of rubber accelerators, synthetic resins and many more.
