Question
Question: An open glass tube is immersed in mercury in such a way that a length of \(8cm\) tends about the mol...
An open glass tube is immersed in mercury in such a way that a length of 8cm tends about the molecular level. The open end of the tube is closed and sealed and the tube is raised vertically up by an additional 48cm. What will be the length of the air column about mercury in the tube now? (Atmospheric pressure= 76cm of Hg)
(A). 38cm
(B). 6cm
(C). 16cm
(D). 22cm
Solution
Give, the tube is first raised by 8cm and then raised by 48cm. In the first condition, the pressure will be due to the air column only but in the second condition, the pressure will be due to mercury as well as air column. Using the ideal gas law equation and formula for pressure in a fluid and equating the pressures at equilibrium point, we can calculate the length of the air column.
Formulas used:
PV=nRT
P=ρgh
Complete answer:
The ideal gas equation is given by-
PV=nRT - (1)
Here, P is the pressure
V is the volume
n is the number of moles
R is the gas constant
T is the temperature
By isothermal process condition, the temperature of both bodies at a given number of moles is same, therefore,
T1=T2
From eq (1), we have
nRP1V1=nRP2V2
⇒P1V1=P2V2 - (2)
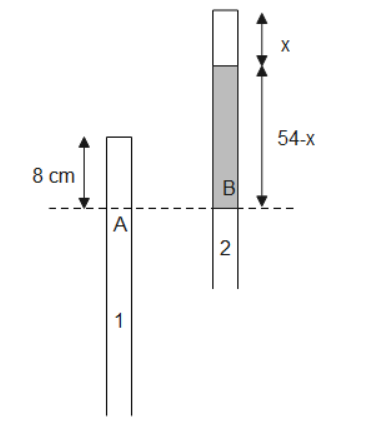
Let P0 be the pressure of tube-1 and P be the pressure of tube-2. We know that volume can be written as a product of area and length. Substituting given values in eq (2), we get,
P08A=PxA
⇒P=x8P0 - (3)
We know that pressure in a fluid is given as-
P=ρgh - (4)
Here, ρ is the density of the fluid
g is acceleration due to gravity
h is the height in the fluid
Using the above equation, we get,
P0=ρmg(76) - (5)
Using eq (3), eq (4), eq (5) equating pressures at point A and B, we get,
ρmg(76)=x8P0+ρmg(54−x)⇒ρmg(76)=x8ρmg(76)+ρmg(54−x)⇒76=x8×76+(54−x)⇒22+x=x608⇒x2+22x−608=0⇒x2+38x−16x−608=0⇒(x+38)(x−16)=0∴x=16cm
Therefore, the length of the air column about mercury in the tube is 16cm.
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note:
Using the thermodynamic equation is more efficient than using the ideal gas equation in this question. Isothermal process is the process in which temperature remains constant, since bodies are kept at room temperature, we can apply isothermal condition here. The pressures at point A and B are equal because in both tubes equilibrium is established at these points.
