Question
Question: An incompressible non-viscous fluid flows steadily through a cylindrical pipe which has radius 2R at...
An incompressible non-viscous fluid flows steadily through a cylindrical pipe which has radius 2R at point A and radius R at point B farther along the flow direction. If the velocity of the fluid at a point A is V, its velocity at the point B will be:
Solution
Hint: In fluid dynamics the continuity equation explains the rate at which the mass enters the system is equal to the ass that leaves the system.
Complete step by step answer:
We can consider a liquid flowing through a pipe. Let A1andA2 be the areas of cross-sections at point A and B respectively.
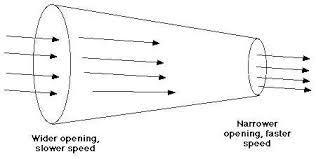
Let the liquid enter with velocity v1 at A and leave with velocity v2at B. volume of liquid entering the tube =A1v1 and volume of liquid leaving the tube = A2v2. Since the same volume of liquid flows across each section of the tube in unit time, we have
A1v1=A2v2
This expression is called the equation of continuity for steady flow of an in-compressible, non-viscous liquid. From this equation it follows that the velocity of flow is small, where the cross-sectional area is large and the velocity of flow is large where the cross-sectional area is small.
Given, At point A, radius r1=2R
Now the Velocity, v1=V
At point B, radius r2=R . Velocity, v2=?
According to equation of continuity,
A1V1 = A2V2
V2=A2A1×V1=πr22πr12×V
V2=(R)2(2R)2×V
V2=(R)24R2×V = 4V
Hence, velocity at point B is 4V.
Additional information:
If fluid flows such that its velocity at a point is always the same in magnitude and direction, the fluid is said to have streamlined flow. Streamline flow is also known as steady flow or orderly flow. Consider a liquid flowing through a pipe of the shape. A particle of the liquid possesses velocity v1 at A and v2 at B and v3 at C. as the liquid flows, different particles will pass through points A, B, and C. If it so happens that all the particles will have velocity v1 when they reach A, velocity v2 when they reach B and velocity v3 when they reach C, then the flow of the liquid is orderly and is called streamline flow.
Note: The continuity equation provides useful information about the flow of fluids and their behavior in the flow of pipe or hose. This equation describes how a fluid conserves a mass in its equation.
