Question
Question: An ideal gas is taken from the same initial pressure P1 to the same final pressure P2 by three dif...
An ideal gas is taken from the same initial pressure P1 to the same final pressure P2 by three different processes. If it is known that point 1 corresponds to a reversible adiabatic and point 2 corresponds to a single-stage adiabatic then:
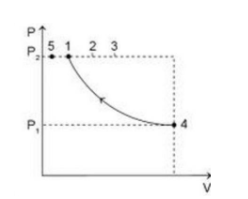
A)Point 3 may be a two-stage adiabatic process
B)The avg. K.E. of the gas is maximum at point 1
C)Work done by surroundings in reaching points 1 or 2 will be positive.
D)The points 3 and 4 may lie along the process having PV2=constant
Solution
To answer this question, you should recall the concept of an adiabatic expansion of a gas. We know that adiabatic expansion is defined as an ideal behaviour for a closed system, in which the pressure is constant and the temperature is decreasing. Use the formula of work done to determine the work done by each process.
Complete Step by step Answer:
We know that during the adiabatic process, no heat enters or leaves the system. Hence during compression, the temperature will increase. The work done in the reversible adiabatic process is given by the expression: wrev=γ−1nR×(T2 - T1)
We can see from the graph plotted that T2 > T1 for the process in which the gas is taken from point 4 to point 1, the work done will be positive. This means that work is being on the system.
Similarly, the work done will be positive when the system is taken from point 4 to point 2.
Hence option C is correct.
We are aware that the ideal gas equation is given by: PV = nRT. Rearranging this equation, we get, TPV=constant. In the process when gas is taken from 4 to 3, as the volume decreases, the temperature increases. Comparing this with the ideal gas equation, we can say that T1 α V. Hence, it may be possible that PV2 =constant. Thus, option D is correct.
Therefore, we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is option C and option D.
Note: We can confuse between different types of reactions. Make sure to remember the difference between isobaric, isochoric, isothermal and adiabatic processes. An isobaric process is one where the pressure of the system (often a gas) stays constant. An isochoric process is one where the volume of the system stays constant. An adiabatic process is a thermodynamic process in which no heat is exchanged between the system and the surrounding.
