Question
Question: An ideal diode is connected in a circuit with resistance \(R=10 \Omega\) and \(V=10\,volts\) as show...
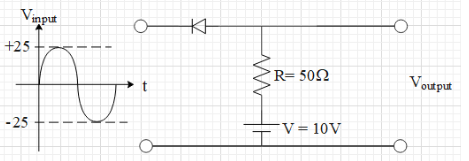
An ideal diode is connected in a circuit with resistance R=10Ω and V=10volts as shown in the figure. The maximum and minimum value of output voltage, when no load applied is
A. 10 V, -25 V
B. 10 V, -15 V
C. 25V, -25 V
D. 25V, 10V
Solution
An ideal diode is a device that allows current to pass through it with zero resistance only when it is connected in forward biased condition. If the diode is reversed biased, then no current will pass through the diode. Check what happens to the output voltage when the input source is at its peaks voltages.
Complete answer:
In the given figure, we can see that the input source of voltage is an alternating source with a peak voltage of 25V.Therefore, the maximum potential difference (magnitude) produced by the input source is 25V. However, there will be a time when the point P will be higher potential and the point Q at lower potential.
When this happens, the diode will be in a reversed biased state and there will be no current in the circuit. In this case, the voltage is provided by the DC source of 10 volts. Therefore, the output voltage is 10 V (when there is no load resistance R).
There will be a time when the input voltage is -25 V with point P at lower potential than that of point Q. When this happens the diode is in forward biased state and will conduct electricity. As a result, the output voltage is -25V. Therefore, the maximum and minimum output voltages are 10V and -25V.
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: Most of the students get confused when a diode is forward or reversed biased.When the anode of the diode is at higher potential than that of its cathode, the diode is forward biased. When the anode of the diode is at lower potential than that of its cathode, the diode is reversed biased.
