Question
Question: An alkene A on ozonolysis gives a mixture of ethanal and pentan-3-one. Write structure and IUPAC nam...
An alkene A on ozonolysis gives a mixture of ethanal and pentan-3-one. Write structure and IUPAC name of A.
Solution
As the name suggests, ozonolysis; which is composed of ‘ozone’ and ‘lysis’ is a method to cleave a double or triple bond. The unsaturated bond breaks and links to ozone so as to form an intermediate, which leads to breaking up of the compound.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the question, a compound ‘A’, which is an alkene, reacts with ozone (O3) to produce a mixture of ethanal and pentan-3-one. We can present this reaction as –
A+O3Zn+H2OH3C−CH=O+CH3−CH2−CO−CH2−CH3
Addition of ozone (O3)to compound ‘A’ results in the formation of an intermediate compound, which is known as ozonide. Ozonide is a cyclic structure which undergoes cleavage to give the final products. The structure of ozonide can be made by joining ethanal and pentan-3-one using oxygen at its double bond with oxygen.
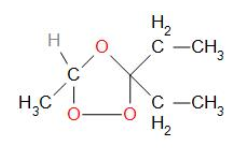
Ethanal and pentan-3-one are obtained from the intermediate ozonide. The structure of 'A' can be derived by removing ozone from the ozonide structure. The structural formula of 'A' is presented as:
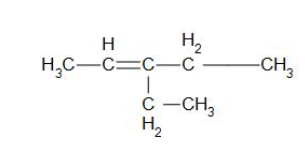
The IUPAC name of this compound is 3-ethylpent-2-ene.
Therefore, the answer is – 3-ethylpent-2-ene on ozonolysis gives a mixture of ethanal and pentan-3-one.
Additional Information: In industries, ozonolysis is widely used for the large-scale manufacture of azelaic acid and pelargonic acids.
Note: Ozonolysis is defined as “a method of oxidatively cleaving alkenes or alkynes using ozone”. This process allows for carbon-carbon double or triple bonds to be replaced by double bonds along with oxygen. This process cannot break a single bond because it is very stable.
