Question
Question: An alkane \({C_6}{H_{14}}\) gives two monochloro derivatives when chlorinated. Which of the followin...
An alkane C6H14 gives two monochloro derivatives when chlorinated. Which of the following is that alkane?
A) 2, 2-dimethylbutane.
B) 3-methyl pentane.
C) 2- methyl pentane.
D) 2, 3- dimethyl butane.
Solution
We know that, Halogenations of an alkane produces a hydrocarbon derivative in which one or more halogen atoms have been substituted for hydrogen atoms. Alkanes are unreactive because they are non-polar and lack functional groups at which reactions can take place.
The general equation for chlorination is,
R−H+X2R−X+H−X
Complete step by step answer: Given,
First, we see hexane.
Hexane is nonpolar molecules with weak intermolecular interactions between the molecules of pure liquid hydrocarbons. It is a highly volatile, flammable toxic chemical. The isomers of Hexane are used as an organic solvent since they are very non-polar.
The molecular structure of hexane,
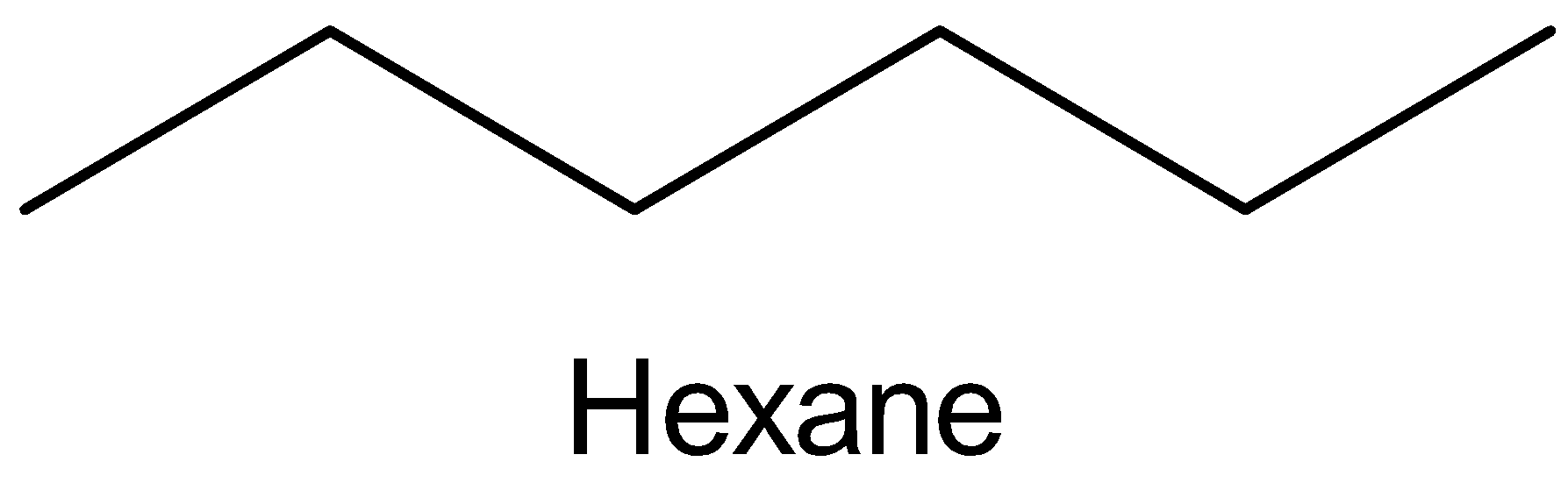
On chlorination, one hydrogen atom in the hexane is replaced by chlorine atom to give monochloro derivatives. Hexane on monochlorination gives two derivatives which mean there must be two different hydrogen atoms for two monochloro derivatives to form.
Let us see the structure of 2, 3-dimethyl butane.
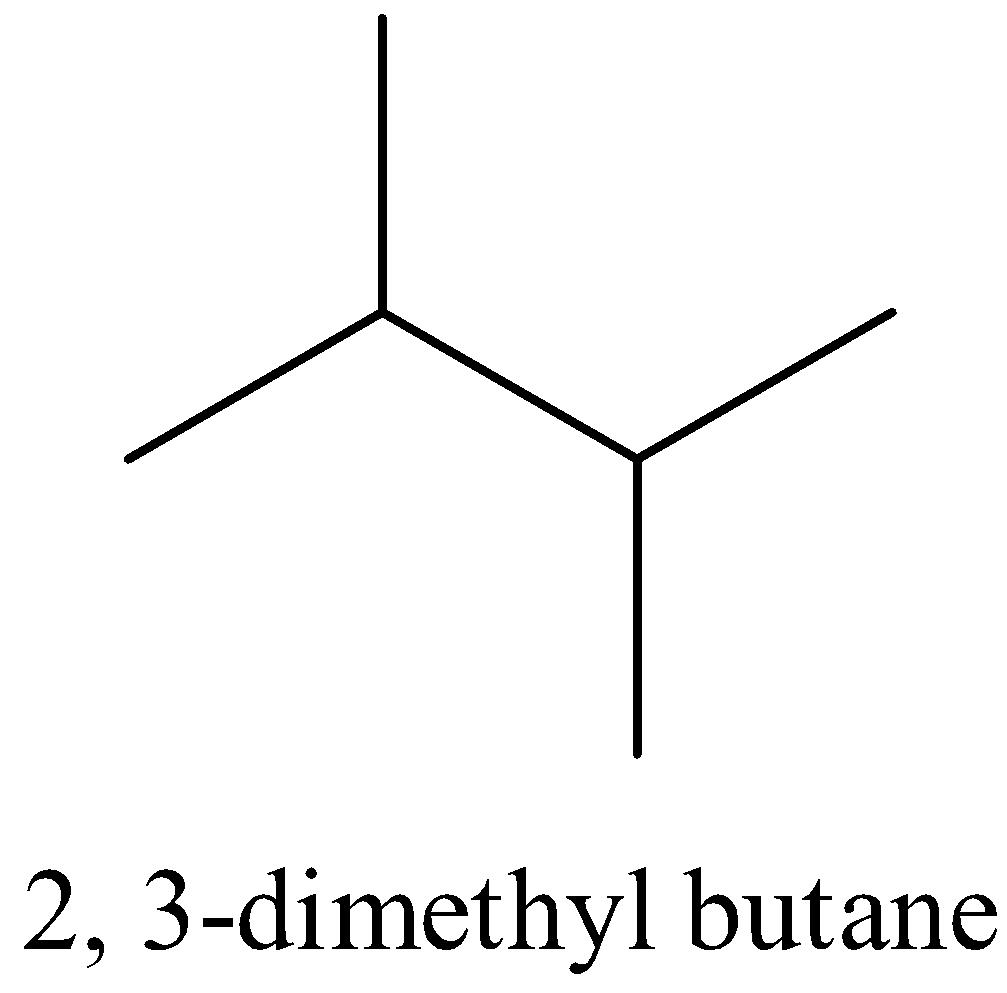
There are two tertiary and twelve primary hydrogen atoms so it can form two monochloro derivatives.
∴The option D is correct.
Note:
We must know that hexane undergoes a combustion reaction readily to form carbon dioxide and water molecules.
Hexane is a good solvent for nonpolar molecules but hexane is not a good solvent to dissolve a polar compound. With a polar compound, water would be a safer option than hexane, because water is polar and can interact more readily with the polar compound.
