Question
Question: An alcoholic solution of dimethylglyoxime is added to an aqueous solution of nickel (II) chloride. S...
An alcoholic solution of dimethylglyoxime is added to an aqueous solution of nickel (II) chloride. Slow addition of ammonium hydroxide leads to the precipitation of a rosy red coloured metal complex. Then find out the number of hydrogen bonds present in the structure of the complex.
(A) 2
(B) 3
(C) 3
(D) None
Solution
The red coloured complex is the product in the form of precipitate which is produced when an alcoholic solution of dimethylglyoxime is added to an aqueous solution of nickel (II) chloride.
Also, it’s a hint that the valency of nickel will determine the complex formation and the number of hydrogen bonds formed.
Complete step-by-step answer: Let us discuss the reactants involved to form a product whose hydrogen bonds needs to be counted;
Dimethylglyoxime is the whitish crystalline solid with molecular formula of C4H8N2O2 (also known as 2, 3 – butadiene dioxide).
When dmgH2 reacts with metals salts, a complex is formed i.e. metal-dmg is formed. So, in the case of nickel (II) chloride; the following displayed complex is formed.
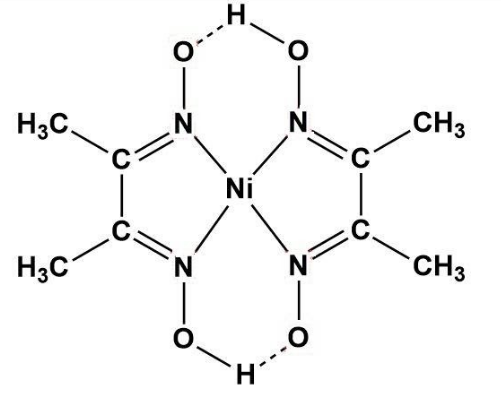
Here, we can see that when Ni2+ reacts with dmgH2, a Ni-dmg complex is formed having two hydrogen bonds (also as the valency of nickel is 2 in ionic form).
Therefore option (2) is correct.
Note: Dimethylglyoxime is actually used for the analysis and identification of nickel and palladium.
Specifically, for the nickel atom, the white coloured powder changes to a rosy red colour complex; hence, the presence of nickel is determined.
