Question
Question: Amongst the following the lowest degree of paramagnetism per mol of the compound at \(298{\text{ K}}...
Amongst the following the lowest degree of paramagnetism per mol of the compound at 298 K will be shown by:
A) FeSO4.6H2O
B) NiSO4.6H2O
C) MnSO4.4H2O
D) CuSO4.5H2O
Solution
We know that the complexes having unpaired electrons are paramagnetic in nature and those having no unpaired electrons are diamagnetic in nature. The crystal field theory helps to describe if the compound is paramagnetic or diamagnetic.
Complete step by step answer:
The ligand bonds to the central metal atom and donates a pair of electrons to the central metal atom and thus, form a coordination complex.
We are given four complexes, FeSO4.6H2O, NiSO4.6H2O, MnSO4.4H2O and CuSO4.5H2O. In the given complexes, the ligand is the water molecule.
Water is a weak field ligand. Thus, it will not cause the pairing of the electrons of the metal atom and high spin complexes are formed.
The oxidation state of Fe in FeSO4.6H2O is +2. Thus, the outer shell electronic configuration of Fe2+ is 3d64s0. Thus,
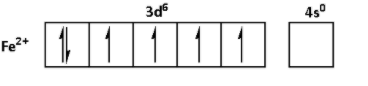
The oxidation state of Ni in NiSO4.6H2O is +2. Thus, the outer shell electronic configuration of Ni2+ is 3d84s0. Thus,
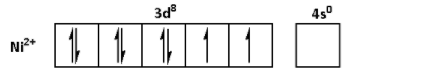
The oxidation state of Mn in MnSO4.4H2O is +2. Thus, the outer shell electronic configuration of Mn2+ is 3d54s0. Thus,
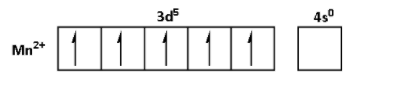
The oxidation state of Cu in CuSO4.5H2O is +2. Thus, the outer shell electronic configuration of Cu2+is 3d94s0. Thus,
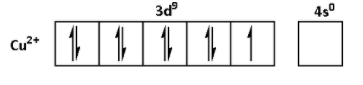
From the electronic configurations, we can see that the Mn2+ has five unpaired electrons. Thus, MnSO4.4H2O shows highest degree of paramagnetism. Fe2+ has four unpaired electrons. Thus, the degree of paramagnetism of FeSO4.6H2O is lower than that of MnSO4.4H2O. Ni2+ has two unpaired electrons. Thus, the degree of paramagnetism of NiSO4.6H2O is lower than that of FeSO4.6H2O. Cu2+ has one unpaired electron. Thus, CuSO4.5H2O shows lowest degree of paramagnetism.
Thus, the correct option is (D) CuSO4.5H2O.
Note: Strong field ligands form low spin complexes. The examples of strong field ligands are CO−, CN−. Weak field ligands form high spin complexes. The examples of weak field ligands are F−, Cl−, H2O.
