Question
Question: Among the following metal carbonyls the \(C - O\) bond order is lowest in A. \([Mn{\left( {CO{)_6}...
Among the following metal carbonyls the C−O bond order is lowest in
A. [Mn(CO)6]+
B. [Fe(CO)5]
C. [Cr(CO)6]
D. [V(CO)6]−
Solution
We know that higher the strength of metal carbonyl, weaker the C−O bond will be. We also know that CO is a strong field ligand and this gives a lot of stability to the complexes.
Complete step by step answer:
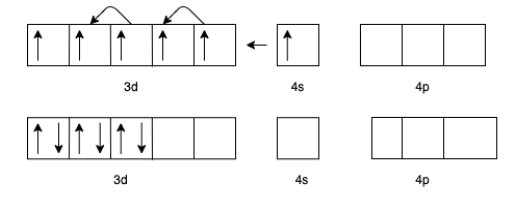
(a) For [Mn(CO)6]+ we know that the charge for Carbon monoxide (CO) is zero.
Therefore, the charge for Mn will be +1.
The electron configuration of Mn+ will be 3d54s1
But in the presence of CO the effective configuration will be 3d64s0. This gives us three lone pairs for back bonding with a vacant orbital of C In CO.
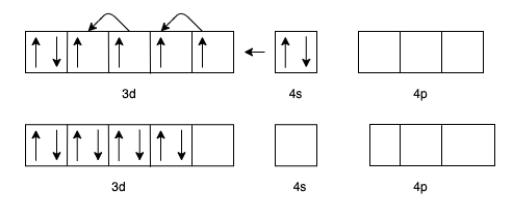
(b) For [Fe(CO)5] the charge of Fe is zero.
The electron configuration of Fe will be 3d64s2
But in presence of CO the effective configuration will be 3d8. This gives us 4 lone pairs for backing bonding with a vacant orbital of C In CO.
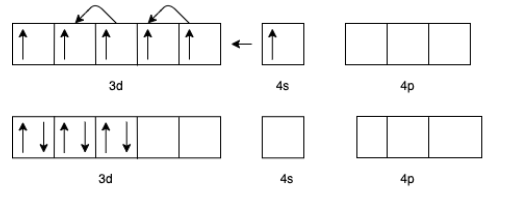
(c) For [Cr(CO)6] the charge of Cr is zero.
The electron configuration of Cr will be 3d54s1
But in presence of CO the effective configuration will be 3d6. This gives us 3 lone pair for backing bonding with a vacant orbital of C In CO.
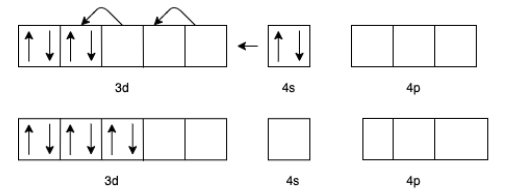
(d) For [V(CO)6]− we know that the charge for Carbon monoxide (CO) is zero.
Therefore, the charge for V will be -1.
The electron configuration of V− will be 3d44s2
But in presence of CO the effective configuration will be 3d6. This gives us 3 lone pair for backing bonding with a vacant orbital of C In CO.
From this we can observe that the [Fe(CO)5] is having the maximum back bonding, hence the bond order will also be lowest for [Fe(CO)5].
Note:
For solving this problem, we can use a shortcut also.
As we said that higher the strength of metal carbonyl, weaker the C−O bond will be. From the options we can see that all of them has a coordination number of 6 except [Fe(CO)5]. In [Fe(CO)5] we can see that the bond between Fe and carbonyl group is distributed among 5 carbonyl group whereas the rest of them Is distributed among 6 carbonyl group. So the per bond strength of the Fe will be greatest, which implies that C−O bond will be weaker
