Question
Question: Among the following L-serine is: A)  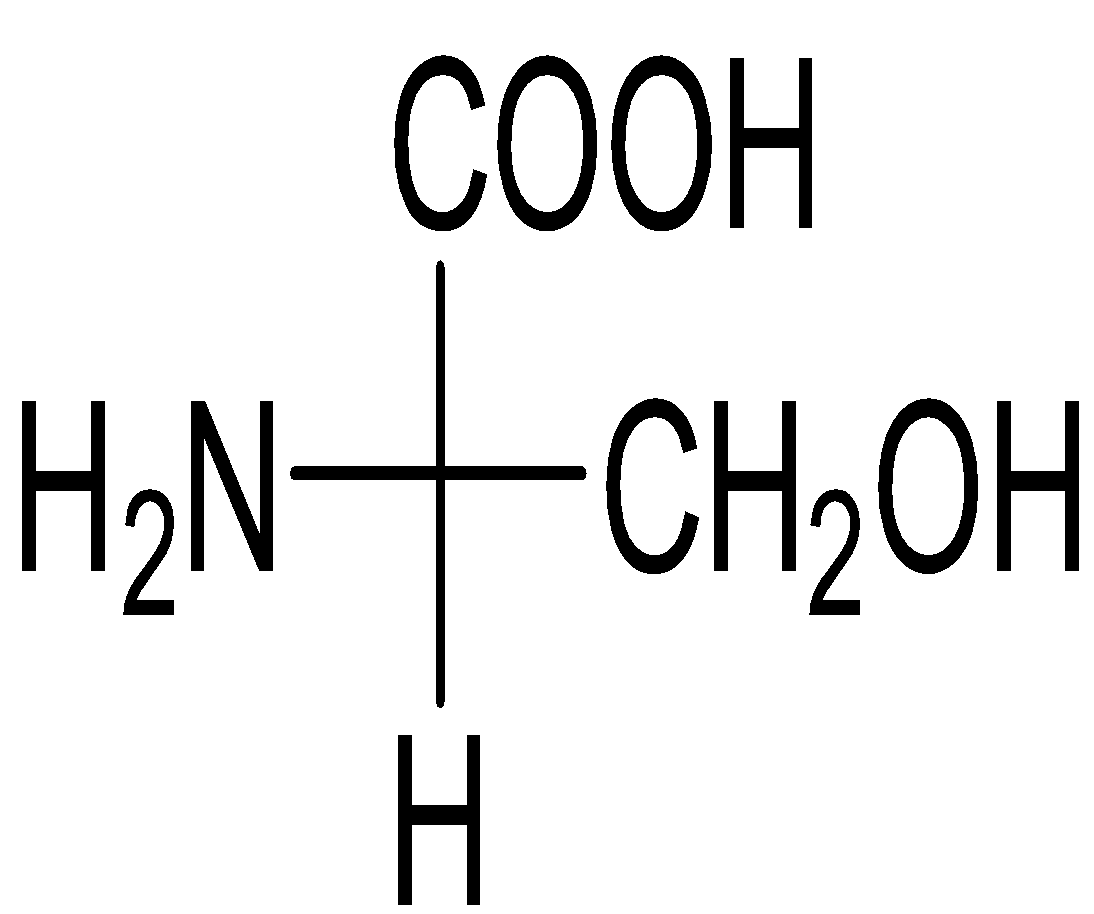
B) 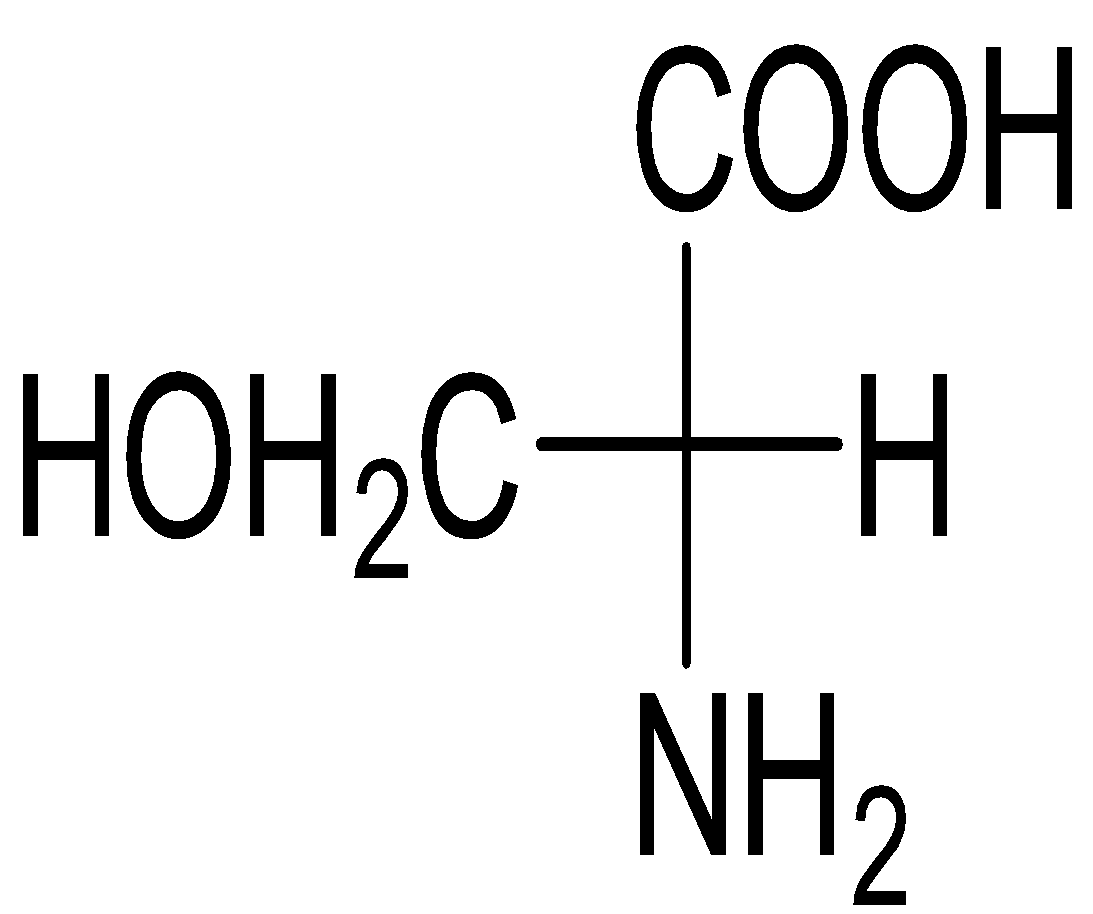
C) 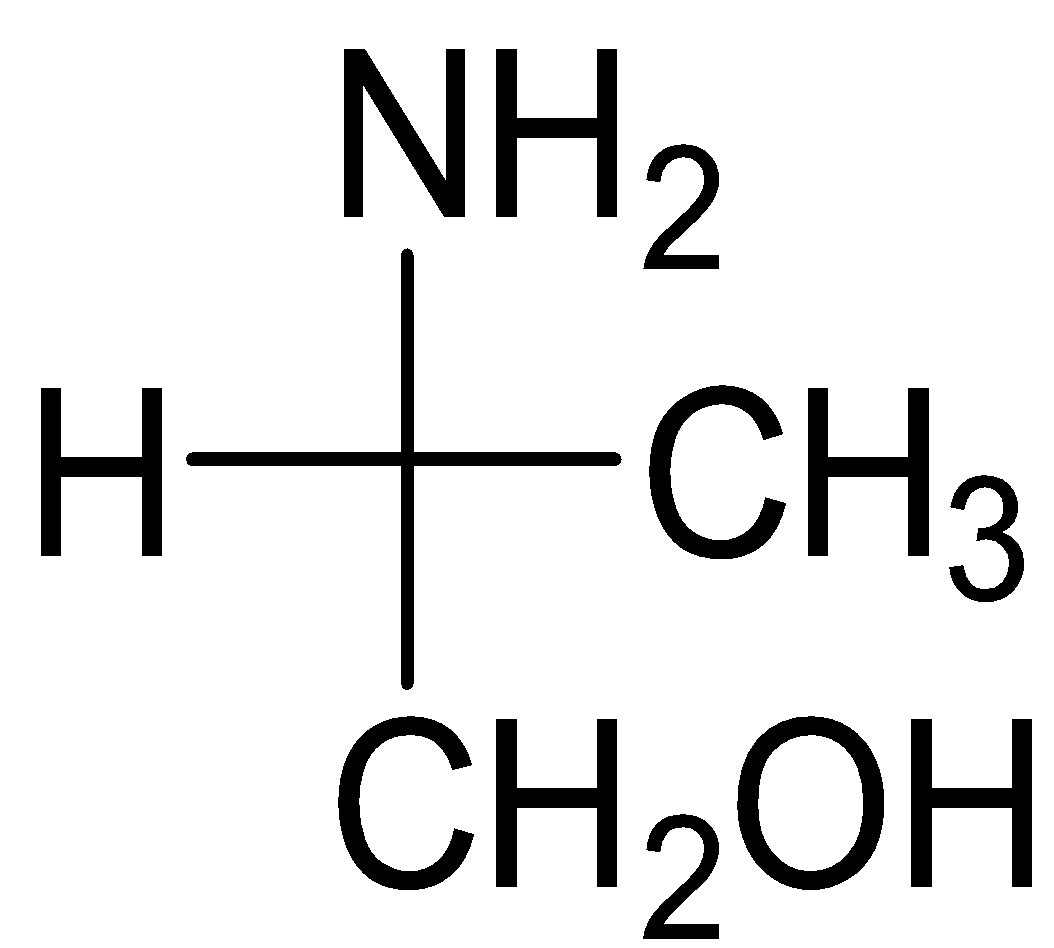
D) 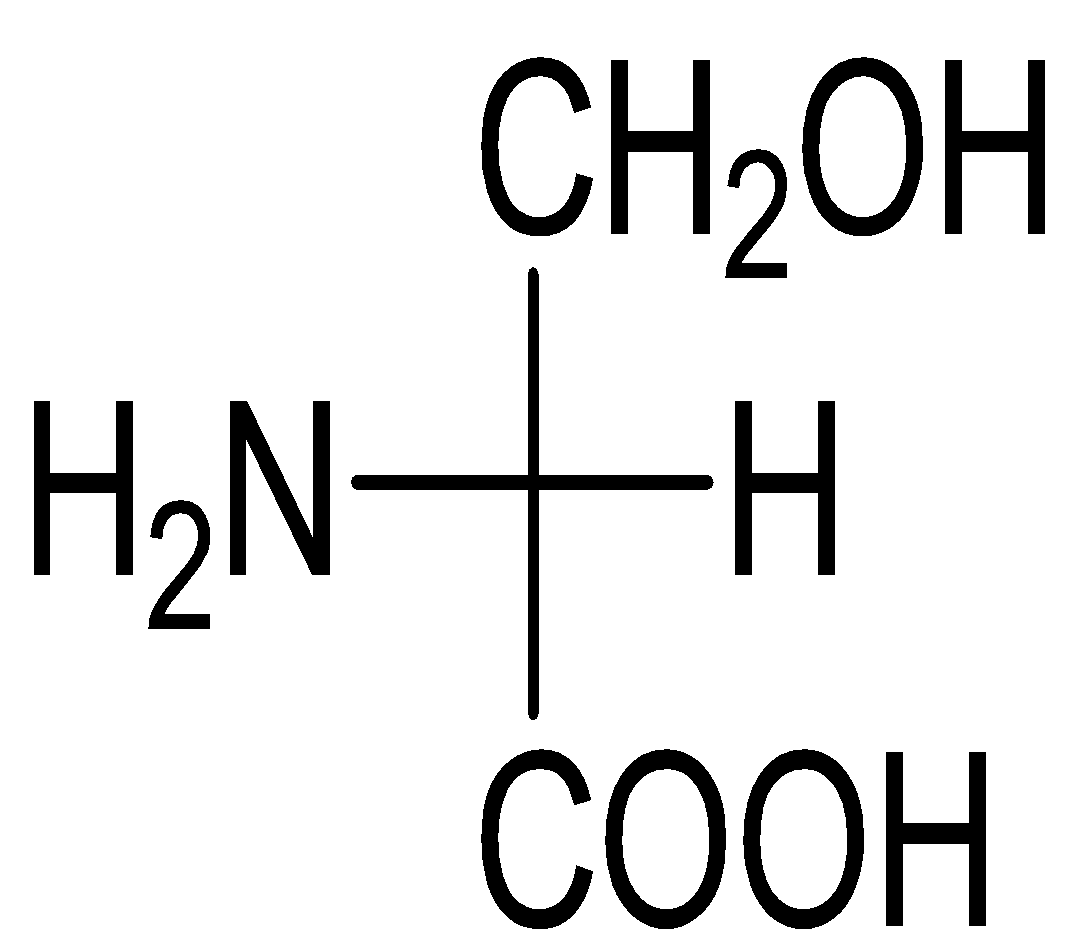
Solution
Serine belongs to the category of ɑ-amino acids which is generally employed in the protein biosynthesis. It comprises of α-amino group (protonated −NH3+), a carboxyl group (deprotonated−COO−), and a side chain comprising of a hydroxyl methyl group, thus, classifying serine a polar amino acid. The L-stereoisomer of serine occurs naturally in proteins.
Complete step by step answer:
Almost every amino acid can exist in two forms of isomers owing to the capability to form two different enantiomers (i.e. stereoisomers) around the chiral (central) carbon atom. Conventionally, these are known as L- and D- forms, which mean left-handed and right-handed atomic configurations. While (+) and (-) notation indicate the substance’s optical activity. If it rotates the plane of polarised light in the clockwise direction, (+) notation is used otherwise (i.e. anti-clockwise) (-) notation is used. If we compare R and S nomenclature, R indicates clockwise direction and S indicates anti-clockwise direction. Always keep in mind that the curved arrow is drawn from the highest priority substituent towards the lowest priority substituent as shown below. The order of priority followed is : −NH2, − COOH, − CH2OH, −H.
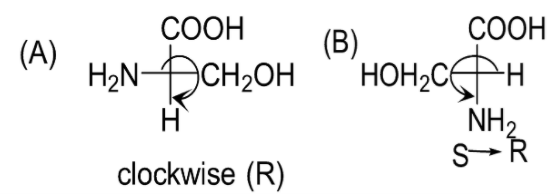
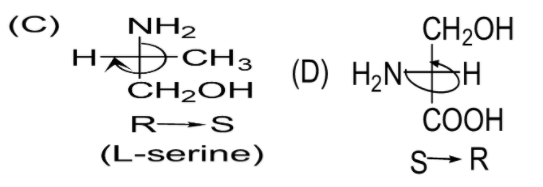
Therefore, the correct answer is Option C.
Note:
The names of the enantiomers of a compound must comprise the "handedness" of a molecule. The Cahn–Ingold–Prelog sequence rules,or simply called as CIP priority rules are considered to be a standard process in organic chemistry to completely name a stereoisomer of a molecule. The CIP rules assign a R or S descriptor to every stereocenter and also an E or Z descriptor to every double bond such that the configuration of the molecule can be uniquely specified by including the descriptors in its name.
