Question
Question: Among the following four compounds i.) Phenol ii.) Methyl phenol iii.) Meta-nitrophenol iv.)...
Among the following four compounds
i.) Phenol
ii.) Methyl phenol
iii.) Meta-nitrophenol
iv.) Para-nitro phenol
The acidity order is:
a.) (iv) > (iii) > (i) > (ii)
b.) (iii) > (iv) > (i) > (ii)
c.) (i) > (iv) > (iii) > (ii)
d.) (ii) > (i) > (iii) > (iv)
Solution
This question deals with the different types of phenol. In phenol the presence of an electron releasing group decreases the acidity whereas the presence of an electron donating group increases the acidity of the phenol.
Complete step by step answer:
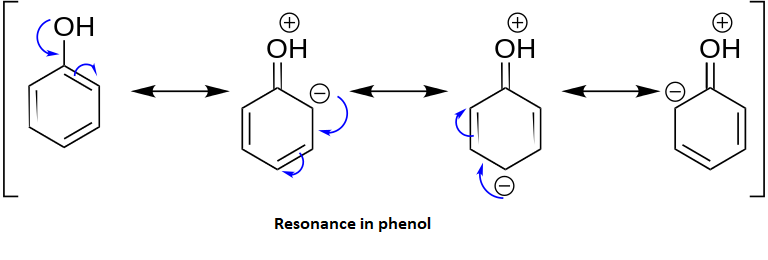
Phenols are more acidic than the saturated alcohols due to the stabilization of the negative charge on the phenolate ion in the benzene ring. For example the phenol group is far more acidic than methanol because the methoxide ion is very unstable whereas the phenolate ion is stable due to resonance. Resonance in phenol:
Para-nitro phenol is most acidic among the following because the base abstracts the proton from the –OH group of phenol. This leads to the formation of phenoxide ion which is stabilized by the nitro group which is present at the para position through resonance effect. As the stability increases acidity also increases.
Meta-nitrophenol is less acidic as compared to para-nitro phenol because the base abstract the proton and form phenoxide ion which is stabilized by the electron withdrawing inductive effect which is less effective as compared to resonance.
Phenol is less acidic as compared to the above two because no electron withdrawing group is present and there is no inductive or resonance effect.
Methyl phenol shows the electron donating inductive effect, hence it is least acidic among the following.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Whenever you have to solve a question regarding the acidic strength always remember that the acid which forms the most stable conjugate base will be more acidic. So compare the stability of the conjugate base in order to compare the stability between different compounds.
