Question
Question: Aldol condensation will not be observed in? A.Chloral B.Phenyl acetaldehyde C.Hexanal D.Etha...
Aldol condensation will not be observed in?
A.Chloral
B.Phenyl acetaldehyde
C.Hexanal
D.Ethanal
Solution
Aldol is the combination of aldehydes and alcohol. The aldol condensation is characterized by the reaction between an aldehyde or ketone with a dilute base. The only important thing is that the aldehyde or ketone should contain an α−Hydrogen atom.
Complete answer:
We know that α hydrogen is the hydrogen present in the carbon atom that is attached to the carbonyl carbon. Now, let us see which compound does not have α hydrogen.
Option A: Chloral
Chloral is also referred to as trichloroacetaldehyde or trichloroethanal. The molecular formula for chloral is Cl3CCHO.
Its structural formula is given by: 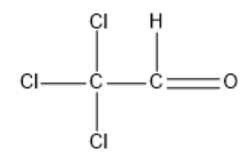
In the above structure, we can observe that the carbon next to the carbonyl carbon does not have any αhydrogen. So, this compound cannot undergo an Aldol condensation reaction.
Option B: Phenyl acetaldehyde
Phenyl acetaldehyde has the molecular formula of C6H5CH2CHO.
Its structural formula is given by: 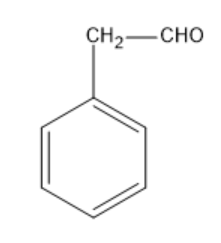
In the above structure, we can observe that the carbon next to the carbonyl carbon has αhydrogen. So, this compound can undergo an Aldol condensation reaction.
Option C: Hexanal
The molecular formula of Hexanal is CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CHO.
Its structural formula is given by: 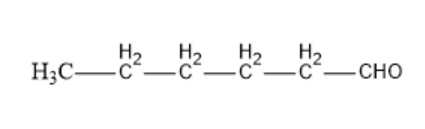
In the above structure, we can observe that the carbon next to the carbonyl carbon has αhydrogen. So, this compound can undergo an Aldol condensation reaction.
Option D: Ethanal
The molecular formula of Hexanal is CH3CHO.
Its structural formula is given by: 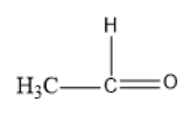
In the above structure, we can observe that the carbon next to the carbonyl carbon has αhydrogen. So, this compound can undergo an Aldol condensation reaction.
Final answer: The correct answer is Option A: Chloral.
Note:
Aldol condensation will not be possible if the αhydrogen is absent. Because in Aldol condensation, the α hydrogen attacks the carbonyl carbon to form an β Unsaturated carbonyl compound. It is favoured by the loss of water molecules from both reactants.
