Question
Question: Air friction increases the velocity of the satellite. Explain....
Air friction increases the velocity of the satellite. Explain.
Solution
Whenever a moving particle hits another particle then some change in speed of both the particles will take place. At the same time the principle of conservation of energy is obeyed and thus we can determine their new speeds. Same thing happens in case of air friction or air drag. Moving satellites in space and a stone we throw on earth are two different cases, stone on earth will face more hindrances as compared to satellites and that is why it stops earlier.
Complete step by step answer:
When a satellite is in space at a certain height above the Earth and moves with a constant speed but when this satellite hits another body in space then a little part of the energy of the satellite is transferred to that particle and that particle will gain some speed.
Now that satellite will slow down a little bit now if a satellite hits another body in space the same phenomena will occur and the speed of the satellite again slows down. As the satellite's speed slows down it will begin to fall towards the Earth(due to circular motion, speed decreases hence radius decreases). Thus the PE of that satellite will decrease and hence the kinetic energy will increase(gravity is conservative force) therefore, the component of velocity which is towards Earth will increase.
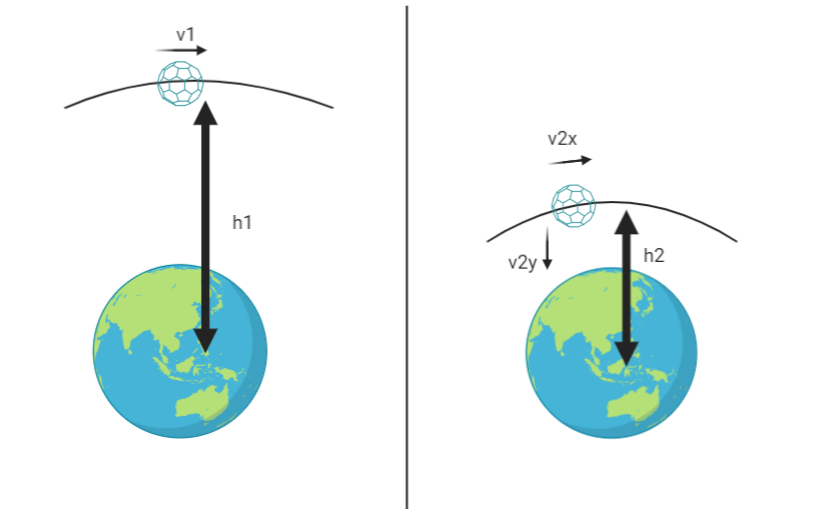
Here h1 > h2
Initial velocity of satellite is v1 after collision (v2)xwill be the new velocity (orbital velocity) and (v2)y will be the falling velocity of the satellite.
Thus overall speed of the satellite increases
vtotal=(v2)x2+(v2)y2
So V2 > V1
Note: Speed, being a scalar quantity, it is the rate at which an object covers distance. The average speed is the distance (a scalar quantity) per time ratio. Speed is ignorant of direction. On the other hand, velocity is a vector quantity; it is direction-aware. Velocity is the rate at which the position changes. The average velocity is the displacement or position change (a vector quantity) per time ratio.
