Question
Question: Agarose is a polymer of: (A) Glucose (B) Agarobiose (C) Polyacrylamide (D) Bisacrylamide...
Agarose is a polymer of:
(A) Glucose
(B) Agarobiose
(C) Polyacrylamide
(D) Bisacrylamide
Solution
We need to understand what is polymerization and the components of agarose. The term polymer is defined as macromolecules which are formed by the joining of repeating structural units on a large scale. They are very large molecules having a high molecular mass-as high as 103−107 u. The repeating structural units are called monomers or monomeric units which are linked to each other by covalent bonds to form polymers.
Complete answer:
We have to remember that Agarose is a form of polysaccharide which is a linear polymer of repeating units of agarobiose. Agarobiose is not a monosaccharide. It is a disaccharide (combination of two monosaccharides). Agarobiose is made up of a repeating unit of D-galactose and 3, 6-anhydro-L-galactopyranose joined by 1-4 linkages. We can draw the structure of agarobiose as,
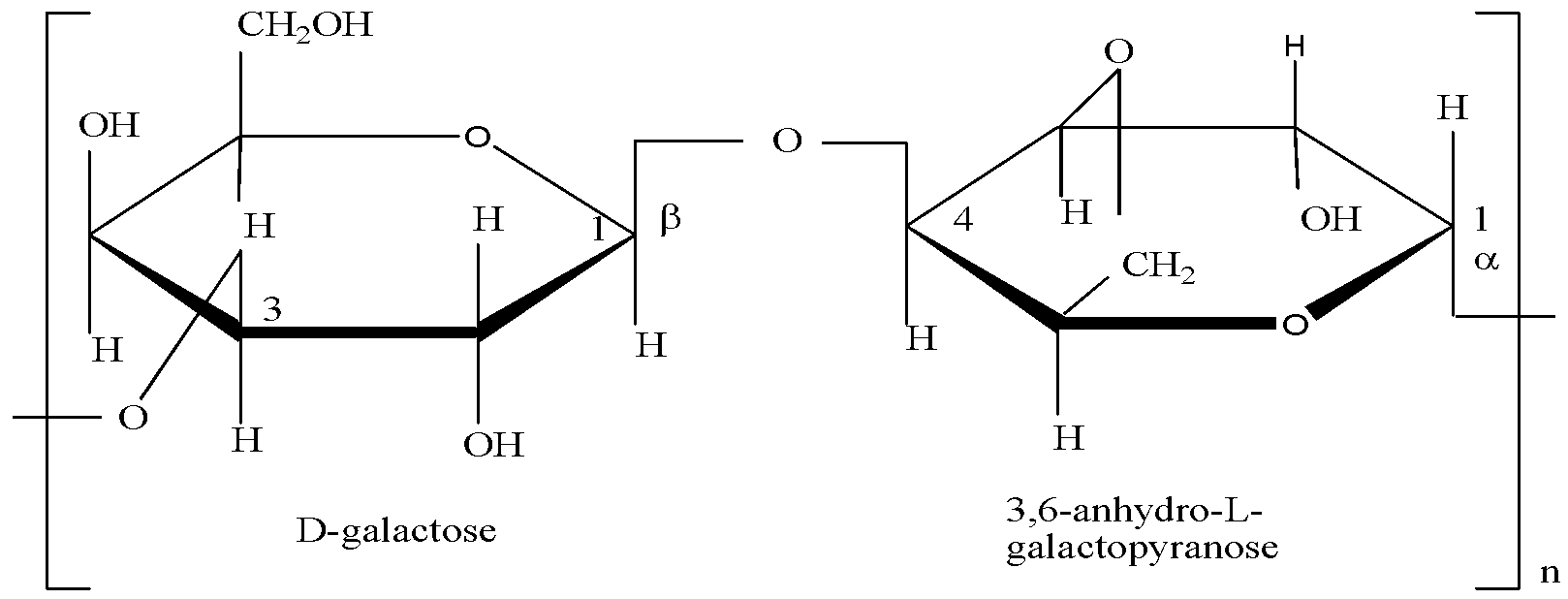
As given in the options, it is clear that agarose is a polymer of the disaccharide agarobiose.
Hence, the correct option is option (B).
Additional note:
We have to know that the process of forming polymers from their respective monomeric units is known as polymerization. Different monomeric units are involved in different polymers. In case of carbohydrates, the smallest monomer is called a monosaccharide and different or same repeated units of monosaccharide form a polysaccharide. If the molecular mass of the polysaccharide is as high as 103−107u, it can be called a polymer. For example, polymers of glucose. Glucose acts as a monomeric unit in glycogen, starch and cellulose. Glucose is a monosaccharide. Glycogen, starch and cellulose are polymers that have the same monomeric unit which is glucose but differ in the way these glucose units are linked to each other linear or branched.
Note:
It must be noted that the monomeric units of a polymer must be known in order to conclude the constituents of a polymer. Also, as given in the options above, (A)glucose units form starch, glycogen and cellulose, (C) polyacrylamide is itself a polymer of acrylamide subunits and (D) bisacrylamide is a cross-linking agent used during the formation of polymers such as polyacrylamide.
