Question
Question: Acid catalysed dehydration of t-butanol is faster than n-butanol because:- A.tertiary carbocation...
Acid catalysed dehydration of t-butanol is faster than n-butanol because:-
A.tertiary carbocation is more stable than primary carbocation
B.primary carbocation is more stable than tertiary carbocation
C.t-butanol has a higher boiling point
D.rearrangement takes place during dehydration of t-butanol.
Solution
Dehydration reaction is a type of elimination reaction . It goes through the formation of carbocations. When dehydration occurs the rearrangement occurs in the reaction. Tertiary carbocations are most stable due to presence of more +I generating group ( inductive effect) .secondary and primary carbocation are less stable due to less +I effect and primary carbocation is least stable. The dehydration of alcohols depends on stability of carbocation and it follows order:-
Tertiary> secondary > primary.
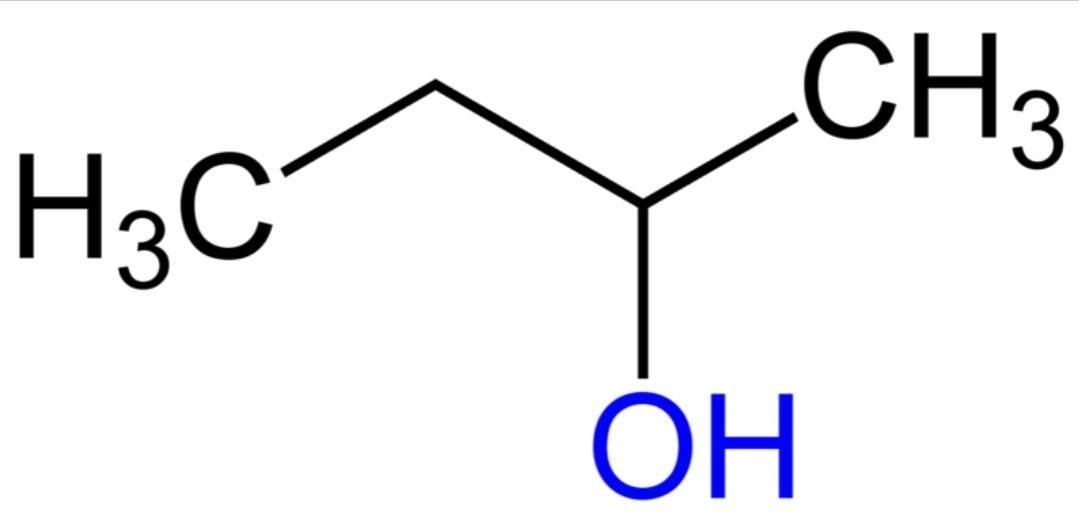
Figure showing t-butanol
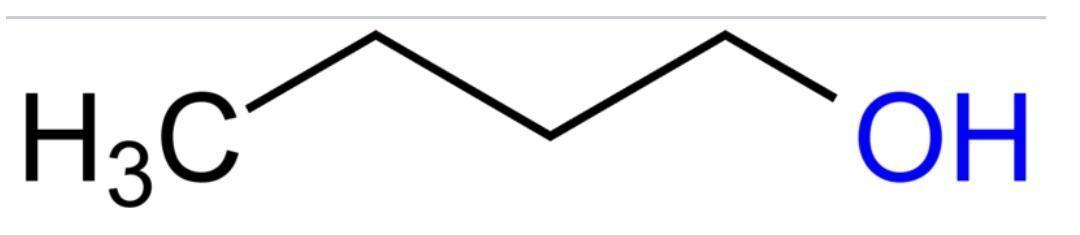
Figure showing n-butanol.
Complete step by step answer:
tertiary carbocation is more stable than primary carbocation:- when dehydration of alcohol occurs they occur according to carbocation stability. In t-butanol tertiary carbocation is formed so it has a faster reaction. Hence this option is correct.
primary carbocation is more stable than tertiary carbocation :-. Primary carbocations are less stable as they have less inductive effect due to presence of less alkyl groups. So this option is not correct.
t-butanol has a higher boiling point :- boiling point does not affect rate of reaction . Only the stability of carbocation affects the rate of reaction. So this option is also not correct.
rearrangement takes place during dehydration of t-butanol. :- t-butanol forms tertiary carbocation which is most stable so rearrangement does not occur in them .Hence this option is not correct.
Our required answer is A, tertiary carbocation is more stable than primary carbocation .
Note:
When alcohol gets heated with strong acid catalysts it leads to removal of water molecules. The alcohols undergo 1,2 – elimination reactions. The products formed are alkene and water. Since there is removal of water molecules it is also known as dehydration reaction.
