Question
Question: Acetoxime on catalytic reduction gives A. Acetic acid B. Acetic anhydride C. Ethyl amine D. ...
Acetoxime on catalytic reduction gives
A. Acetic acid
B. Acetic anhydride
C. Ethyl amine
D. Isopropyl amine
Solution
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction commonly used for the reduction of unsaturated organic compounds. This reaction occurs in the presence of metal catalysts like nickel, palladium or platinum. The hydrogenation reaction is a highly exothermic reaction because formation of stable saturated organic compounds takes place after the reaction.
Complete answer: Acetoxime is an organic compound with the chemical formula (CH3)2CNOH. It is basically a ketoxime with white crystalline solid appearance and it is soluble in solvents like water, ethanol, chloroform, etc. Structurally Acetoxime is represented as follows:
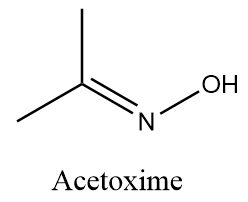
When Acetoxime undergoes catalytic hydrogenation reaction in the presence of palladium and carbon, then the attack of hydrogen atoms take place at the unsaturated double bond and formation of isopropyl amine takes place along with the removal of hydroxide ions. The reaction takes place as follows:
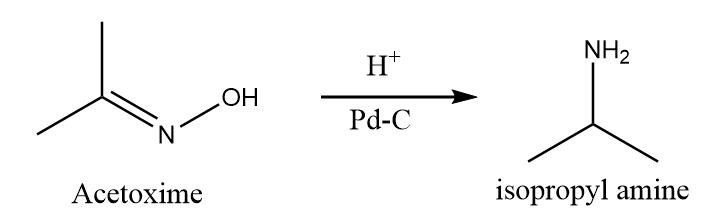
Hence, Acetoxime on catalytic reduction gives isopropyl amine. Therefore, option (D) is the right answer.
Additional information-
In the catalytic hydrogenation reaction, two types of catalyst can be used which are homogeneous catalysts and heterogeneous catalysts. The unsaturated substrate gets dissolved in the solvent in case of homogeneous catalysts whereas in heterogeneous catalysts, either solids are suspended in the same solvent as that of substrate or are treated with gaseous substrate involving adsorption process.
Note:
It is important to note that dihydrogen is unreactive towards organic compounds in the absence of a metal catalyst. In the catalytic hydrogenation, unsaturated molecules are chemisorbed on the surface of the catalyst. Then hydrogen forms surface hydrides with the metals from which hydrogen atoms are transferred to the chemisorbed molecules.
