Question
Question: Acetic acid undergoes dimerisation, when dissolved in benzene (as shown in figure) Molecular mass ...
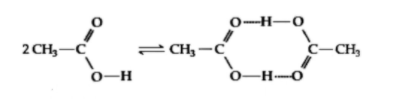
Acetic acid undergoes dimerisation, when dissolved in benzene (as shown in figure)
Molecular mass of acetic acid is found to be 120.
Which among the following relations is correct?
(where, α = degree of association,
d = observed vapour density,
D = Theoretical vapour density).
A. α=2(dD−d)
B. α=2(DD−d)
C. α=2(dd−D)
D. α=D−d2d
Solution
In order to answer this question you must recall the properties of Acetic acid. And recall its reaction with benzene. Acetic acid forms a dimer in the gas phase, where the monomer units are held together by hydrogen bonds. Under special conditions, most OH-containing molecules form dimers, e.g. the water dimer. And to find the answer you must use the association formula by putting the number of atoms getting associated. And finally you will reach your desired answer.
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1: In this step we will use the association formula, to evaluate the correct relation. And the formula for association is: α=d(1−n1)d−D where n is the number of molecules getting associated. And we know that this is a dimerisation reaction, so by Putting the value n = 2 in the above formula we will calculate the value of α and will reach to our answer :
Therefore, α=d(1−21)d−D=d(21)d−D=2(dd−D)
Step 2: Hence we got the value of α, i.e. α=2(dd−D)
(where, α = degree of association,
d = observed vapour density,
D = Theoretical vapour density).
The correct answer is option C .
Note: A dimer (di-, "two" + -mer, "parts") is an oligomer consisting of two monomers joined by bonds that can be either strong or weak, covalent or intermolecular. The term homodimer is used when the two molecules are identical (e.g. A–A) and heterodimer when they are not (e.g. A–B). The reverse of dimerisation is often called dissociation. When two oppositely charged ions associate into dimers, they are referred to as Bjerrum pairs.
