Question
Question: According to the molecular orbital theory, \({{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}\) molecule has: A. \(1\sigma \) a...
According to the molecular orbital theory, C2 molecule has:
A. 1σ and 1π bond
B. Only 2σ bonds
C. Only 2π bonds
D. 1σ and 2π bond
Solution
We can deduce the bonding in a molecule by looking at the molecular orbital diagram for the same as to whether sigma or pi- molecular orbitals are being used for bonding.
Step by step answer: We have various theories for bonding and here we will take up the molecular orbital theory. We can use the molecular orbital theory for drawing molecular orbital diagrams for a molecule which is quite useful in deducing various properties such as bond order or explaining magnetic behavior of the molecule. Let’s have a look at the molecular orbital diagram of C2 molecule that is given below:
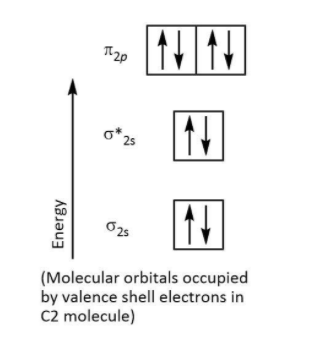
We know that one carbon atom has 6 valence electrons which mean a C2 molecule has 12 electrons in the molecular orbitals. We can write the electronic configuration for C2 molecule with 12 electrons as follows:
(σ1s)2(σ1s∗)2(σ2s)2(σ2s∗)2(π2px2=π2py2)
Now, we can determine the bond order for C2 molecule by using the following formula:
B.O.=2NelectronsinbondingMO−Nelectronsinanti−bondingMO
As we can see from the electronic configuration for C2 molecule, we have 8 electrons in bonding molecular orbitals and 4 electrons in antibonding molecular orbitals. Let’s calculate the bond order by substituting these values in the above formula as follows:
B.O.=28−4 ⇒B.O=2
So, we can say that the two carbon atoms are connected by a double bond.
Now let’s consider this double bond. We can see there are 4 electrons present in 2π molecular orbitals which means that the double bond is made of 2π bonds.
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note: Usually, we have known that a double bond is consisted of 1σ and 1π bond but this in true case of C2 molecule. So, we need to consider the occupancy of the molecular orbitals as well.
