Question
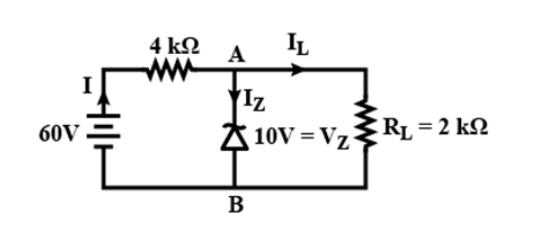
Question: A Zener diode is connected to a battery and a load as shown. The currents \(I,{I_z}\) and \({I_L}\) ...
A Zener diode is connected to a battery and a load as shown. The currents I,Iz and IL are respectively
A. 12.5mA,5mA,7.5mA
B. 15mA,7.5mA,7.5mA
C. 12.5mA,7.5mA,5mA
D. 12.5mA,7.5mA,5mA
Solution
Zener diode is like an ordinary P-N junction diode except that it is properly doped so as to have a sharp breakdown voltage. There are many two-terminal devices, which have a single P-N junction. Zener diode is one of such two-terminal devices. Zener diodes are operated in reverse breakdown because they have very stable breakdown voltage.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the voltage drop across the 4kΩ resistor is 60V−10V=50V.
Therefore, the current from the 4kΩ resistor is:
I=4×103V50V =12.5mA
The current IL is given by:
IL=2×103Ω50V =5mA
The current IZ is given by:
IZ=I−IL =12.5mA−5mA =7.5mA
Hence, the value of I, I L and IZ is 12.5 mA, 7.5 mA, 5mA respectively and the correct option is C.
Additional Information: In a Zener diode, high-level impurities are added to the semiconductor material to make it more conductive. Due to the presence of these impurities, the depletion region of the diode becomes very thin. The intensity of the electric field is increased across the depletion region, due to heavy doping even if a small voltage is applied.
Note: Zener Diodes are widely used as Shunt Voltage Regulators to regulate the voltage across small loads. Zener Diodes have a sharp reverse breakdown voltage and breakdown voltage will be constant for a wide range of currents. Thus we will connect the Zener diode parallel to the load such that the applied voltage will reverse bias it. Thus if the reverse bias voltage across the Zener diode exceeds the knee voltage, the voltage across the load will be constant. The reverse bias voltage across the Zener diode exceeds the knee voltage; the voltage across the load will be constant.
