Question
Question: \((A)\xrightarrow[{AlC{l_3}}]{{C{H_3}COCl}}(B)\xrightarrow[{}]{{PC{l_3}}}(C)\xrightarrow{{2NaN{H_2}}...
(A)CH3COClAlCl3(B)PCl3(C)2NaNH2(D) If (A) is C6H6, then:
(A) D is a terminal alkyne
(B) (A) is a aromatic compound
(C) D has 8 carbon
(D) All the statements are true
Solution
Hint: In presence of lewis acid, acyl chloride will give a Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction. Aromatic compound is a compound which has a ring which has total 4n+2 π electrons and planar structure. Terminal alkyne is a compound in which one sp hybridized carbon has hydrogen bonded with it.
Complete Step-by-Step Solution:
We will see the complete reaction with mechanism in order to find the correct answer.
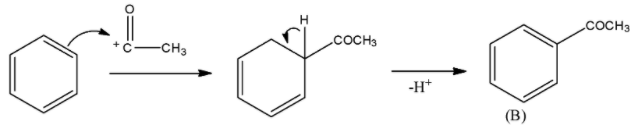
- AlCl3 is a lewis acid and in presence of it, acetyl chloride can give Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction when Benzene is allowed to react. Thus, an electrophilic substitution reaction will take place here. The product formed is Acetophenone. The mechanism of the reaction can be given as
CH3COCl+AlCl3→CH3CO++AlCl4−
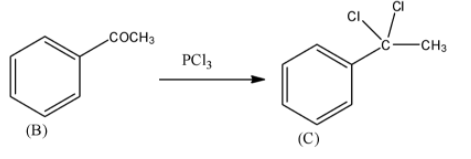
- PCl3 is a compound which has nucleophilic chlorine atoms. Thus, chlorine atoms attack the carbonyl carbon to give a geminal dihalide compound. Thus, the carbonyl carbon will have two chlorine atoms after the reaction with PCl3. The reaction can be given as
- Then, sodamide (NaNH2) is allowed to react with the compound (C). Sodamide is a very strong base and it can bring dehydrohalogenation of the germinal chloride compound. The product will be a terminal alkyne. The mechanism can be given as below.
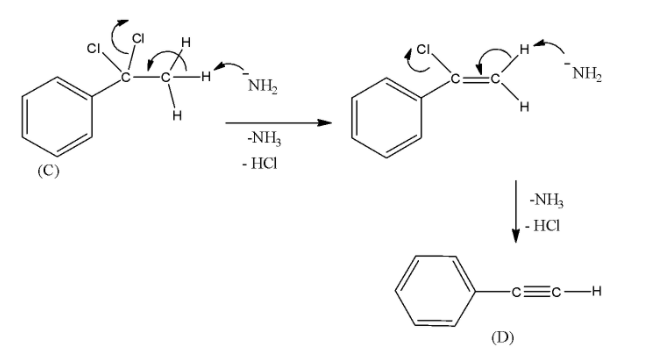
- Thus, we can see that the compound (D) has a group C≡C−H . Thus, this alkyne is called terminal alkyne. As compound (A) has given Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction, (A) is an aromatic compound. We can see that compound (D) has a total of 8 carbon atoms. Thus, all statements are true.
So, the correct answer of the question is (D).
Note: Remember that sodamide is a strong base and when it is allowed to react with geminal halides, it forms alkynes. If there is possibility of formation of a normal alkyne and a terminal alkyne, then formation of terminal alkyne is favored.
