Question
Question: (a)Write two differences between Lyophilic and Lyophobic colloids. (b) Give the name of two enzyme...
(a)Write two differences between Lyophilic and Lyophobic colloids.
(b) Give the name of two enzymes present in yeast. Also write equations of the enzyme catalyzed reaction.
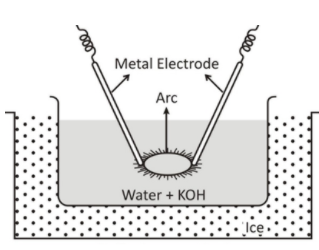
(C) Draw the labeled diagram of Bredig’s Arc method.
Solution
(a) Out of Lyophilic and Lyophobic colloids, one has strong affinity for the dispersion medium. The other has little affinity for dispersion medium.
(b) One enzyme catalyzes the conversion of sucrose into glucose and fructose. The other enzyme catalyzes the conversion of sucrose into ethanol and carbon dioxide.
(c) You can use the Bredig's arc method for the preparation of colloidal solutions of metals such as Gold, Silver and Platinum. Both dispersion and condensation are involved in this method
Complete answer:
(a) Lyophilic Colloids- These colloids have strong affinity for solvent (usually water). They can be easily prepared by direct mixing of the dispersed phase with the liquid dispersion medium. They are stable and cannot be easily precipitated. They are reversible in nature.
On the other hand Lyophobic Colloids have very less affinity with dispersion medium (solvent, usually water) and cannot be prepared by directly mixing the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium. They can get easily precipitated as they lack stability and are irreversible in nature.
(b) The two enzymes that are present in the yeast that are responsible for the formation of ethanol are Invertase and Zymase. Invertase converts sucrose into glucose and fructose and Zymase converts these monosaccharides into ethanol. Write the reaction as follows –
C12H22O11 + H2O Invertase C6H12O6 + C6H12O6
C6H12O6 Zymase 2 C2H5OH + 2 CO2
(c)Bredig's arc method is a method of preparation of colloidal solutions of metals such as Gold, Silver and Platinum.
This method consists of both dispersion and condensation. An arc is struck between electrodes under the surface of water containing some stabilizing agent such as traces of potassium hydroxide. The intense heat of the arc vaporizes some of the metal which then condenses under cold water. The water is kept cold as an ice bath. The colloidal particle prepared is stabilized by adding a small amount of potassium hydroxide to it.
The labeled diagram is given below-
Note:
(a) You can define hydrophilic colloids as the lyophilic colloids in which the dispersion medium is water. Such colloids have strong affinity for water. You can define hydrophobic colloids as the lyophobic colloids in which the dispersion medium is water. Such colloids have little affinity for water.
(b) Sucrose is known as invert sugar due to its mutarotation. The specific rotation of unhydrolyzed sucrose is +66.5o0 (Dextrorotatory) but when it is dissolved in water, it undergoes hydrolysis and its specific rotation becomes −28o and due to this change in specific rotation on hydrolysis, you can call sucrose as invert sugar.
(c) Bredig's arc method is not suitable when the dispersion medium is an organic liquid. If you use an organic liquid, then considerable charring occurs.
