Question
Question: (a). Write the principle of working on a meter bridge. (b). In a meter bridge, the balance point i...
(a). Write the principle of working on a meter bridge.
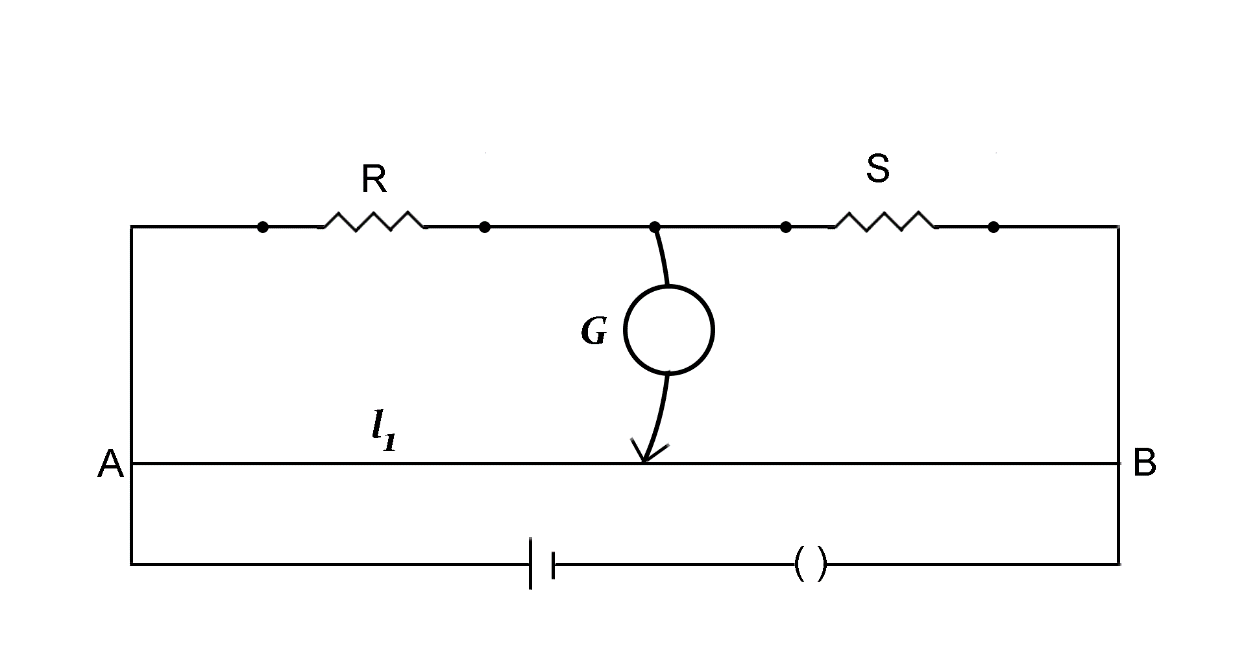
(b). In a meter bridge, the balance point is found at a distance l1 with resistance R and S as shown in the figure. An unknown resistance X is now connected in parallel to the resistance S and the balance point is found at a distance l2 . Obtain a formula for X in terms of l1 , l2 and S .
Solution
- Hint: You can start by defining the principle behind Meter Bridge (the concept of wheatstone bridge). Then use the equation SR=100−l1l1 on the circuit before and after connecting the resistance X in parallel. Compare the equations to reach the solution.
Complete step-by-step answer:
(a). Meter Bridge is also known as a slide wire bridge. Meter Bridge is a practical form of wheatstone bridge. A wire of 1m(100cm) and uniform area of cross-section is made up of constantan or manganin. This wire is stretched between two strips made up of copper which holds the wire in place.
According to the concept of wheatstone bridge circuit, any point on the wire the ratio of two resistors (in this case R and S ) is equal to the ration of the resistance of the wire of any length (in this case l1 ) and the resistance of the remaining wire (in this case 100−l1 ).
(b). In the given problem we have two resistors R and S . The pointer is set at a point where it divides the 100cm into different segments: one of l1cm length and one of 100−l1cm length.
So using the concept of wheatstone bridge, we get
SR=100−l1l1
R=100−l1Sl1
When we connect a resistance X in parallel to S , we have the following circuit.
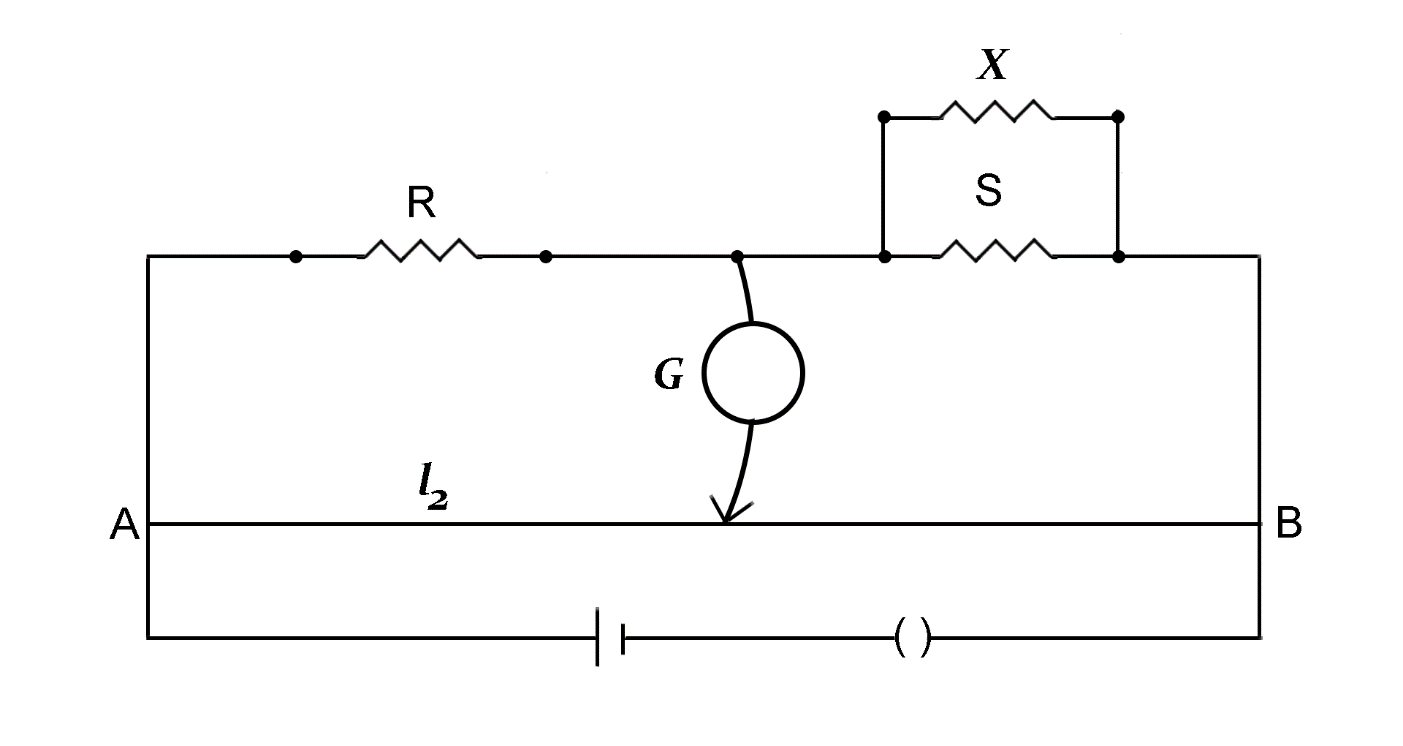
Let’s assume that X and S resistors in parallel produce a combined resistance of Z.
Z=S+XSX
Now, again using the concept of wheatstone, we get
ZR=100−l2l2
Substituting RandZ
100−l1Sl1×SXS+X=100−l2l2
⇒(100−l2)l1(S+X)=(100−l1)l2X
⇒X=100(l2−l1)l1S(100−l2)
Note: Wheatstone bridge is essentially an electric circuit that is in the form of a bridge. The two sides of the bridge are connected by a galvanometer. The wheatstone bridge is named after Sir Charles wheatstone who helped in popularizing it. It helps in calculating the resistance of an unknown resistance.
