Question
Question: A wireframe in the shape of an equilateral triangle is hinged at one vertex so that it can swing fre...
A wireframe in the shape of an equilateral triangle is hinged at one vertex so that it can swing freely in a vertical plane, with the plane of the triangle always remaining vertical. The side of the frame is 31m. The time in seconds of small oscillations of the frame will be: (g=10m/s2)
A) 2π
B) 3π
C) 6π
D) 5π
Solution
The process of repeating variations of any quantity is called Oscillation. It can also be defined as the periodic variation of the matter between the two values. The time required by the object to complete one full cycle is called the period of motion.
Complete step by step solution:
Given data:
The wireframe is in the shape of an equilateral triangle.
The side of the frame =31m
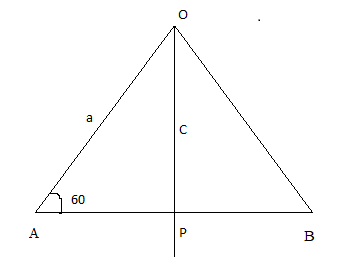
From the figure OP=asin60∘=23a
Then OC=3a
Inertia, I=2(3ma2)+m(OP)2+12ma2 I=2(ma2)
⇒I=32ma2+43ma2+12ma2 (∵OP=23a)
⇒I=23ma2
The time-period is given by the formula, T=2π(3m)glI
⇒T=2π(3m)g(3a)(2ma23)
⇒T=2π23ga
Substituting a=31andg=10m/s2, we get, T=5πsec
Thus the time-period in a sec, T=5πsec
Hence the correct option is D.
Note: 1) The movement of any object from one position to another position for the observer is called motion. There are four basic types of motion namely oscillating, rotary, linear, and reciprocating.
2) The periodic motion is a repeated oscillation at regular intervals and the number of oscillations per unit time is the frequency. The period is defined as the time taken to complete one oscillation. The period depends on the mass of the oscillating system.
3) Vertex is a point where two or more lines or curves or edges meet. It can also be defined as a point where the two lines meet to form an angle.
4) The acceleration gained by the object due to the gravitational force is called acceleration due to gravity. It is denoted by g. It will have the magnitude as well as the direction. The acceleration due to gravity is zero at the center of the earth and is maximum at the poles.
