Question
Question: A wire KMN moves along the bisector of the angle \[\theta \]with a constant velocity v in a uniform ...
A wire KMN moves along the bisector of the angle θwith a constant velocity v in a uniform magnetic field B perpendicular to the plane of the paper and directed inwards. Which of the following is correct?
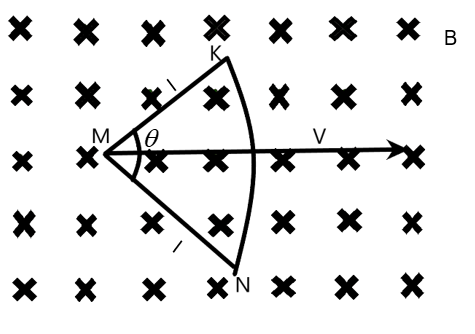
A) Effective length of the wire is 2lsin2θ
B) Emf induced between K and N is 2Blvsin2θ
C) The shape of KMN is immaterial, only the end points K and N are important.
D) All of the above.
Solution
We are given the direction of motion of a conducting wire in a magnetic field with its velocity in the field. We need to find the related changes that occur in this wire due to this motion in the given magnetic field such as the emf and the effective length.
Complete answer:
We know that any conductor moving in a magnetic field which has a perpendicular component of motion to the field can develop a motional emf along its two ends. A conductor moving with a constant velocity and in a constant angle will not produce a change in flux, so there will be no emf produced.
In our case a wire KMN is moving with a constant velocity with an angle, therefore, a motional emf is generated along its motion.
We know that the motional emf of a conductor is given as –
ε=Blv
Where, l is the effective length of the wire used.
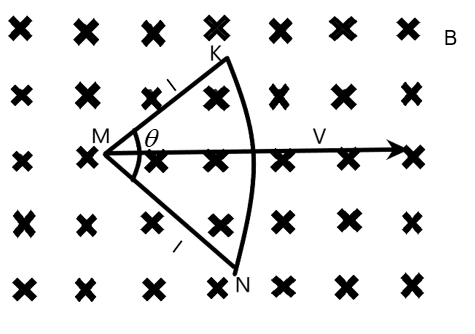
From the below figure, we can understand that the effective length of the wire is along sin2θ, so the length will be 2lsin2θ, given that KM and MN is of length ‘l’.
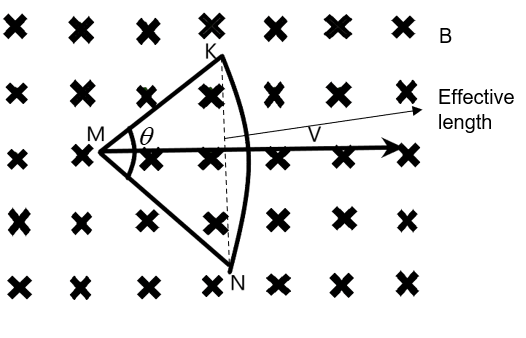
Now, let us calculate the motional emf of the wire KMN as –
