Question
Question: (a) Why are the connections between the resistors in a meter bridge made of thick copper strips? (...
(a) Why are the connections between the resistors in a meter bridge made of thick copper strips?
(b) Why is it generally preferred to obtain the balance point in the middle of the meter bridge wire?
(c) Which material is used for the meter bridge wire and why? OR
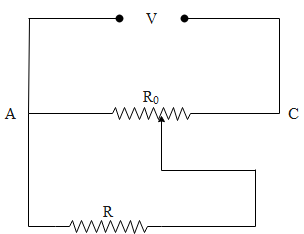
A resistance of RΩ draws current from a potentiometer as shown in the figure. The potentiometer has a total resistance R0Ω. A voltage V is supplied to the potentiometer. Derive an expression for the voltage across R when the sliding contact is in the middle of the potentiometer.
Solution
We know that a meter bridge also called a slide wire bridge is an instrument that works on the principle of a Wheatstone bridge. A meter bridge is used in finding the unknown resistance of a conductor as that of in a Wheatstone bridge. The reason why this bridge is called the Meter Bridge is because of the fact that it works on the Wheatstone bridge's principle. So, people also popularly call it as Wheatstone's meter bridge. Another thing is that the wire length used in this circuit is of 1 meter, so it has got its name as a meter bridge.
Complete step by step answer:
We can determine,
a) The resistivity of copper wire is very low. The connections between the resistors are made of thick wires so as to increase the rate of cross-section. Therefore, the resistance of wires is almost negligible.
b) Balance point is obtained in the middle of the meter bridge wire so as to increase the sensitivity of the meter bridge.
c) Constantan is used for meter bridge wire because its temperature coefficient of resistance is almost negligible due to which the resistance of the wire does not change with increase in temperature of the wire due to flow of current. OR
Total resistance is given by, Rtot =2R0+2R0+R2R0⋅R=2(R0+2R)R(R0+4R)
Total current through the device is given by, ltotal =V/Rtotal
Current through resistance R is given by, I2=Itotal ×R0/2+RR0/2
=Itotal ×R0+2RR0
=R(R0+4R)V⋅2(R0+2R)×R0+2RR0
I2R=R(R0+4R)2VR0
Voltage across resistance is given by V,
I2R=R0+4R2VR0
Note: We should know that a metre bridge experiment is performed in the labs using a scale attached to the block. Two gaps are formed on it by using thick metal strips in order to make the Wheat stone's bridge. The terminal B between the gaps is used to connect the galvanometer and jockey. A resistance wire is introduced in gap S and the resistance box is in gap R. To find resistance of a given wire using a metre bridge and to determine the resistivity of its material. A metre bridge, also known as slide wire bridge is an instrument that works on the principle of Wheatstone bridge. It is used to determine the unknown resistance of a conductor.
It should also be known that Constantan is used for meter bridge wire because its temperature coefficient of resistance is almost negligible due to which the resistance of the wire does not change with increase in temperature of the wire due to flow of current.
