Question
Question: A) What is the action of a) nitrating mixture on chlorobenzene. B) concentrated \({H_2}S{O_4}\) on...
A) What is the action of a) nitrating mixture on chlorobenzene.
B) concentrated H2SO4 on chlorobenzene.
C) alcoholic NH3 on ethyl bromide.
Solution
Nitrating mixture is the mixture of concentrated sulphuric acid and concentrated nitric acid. It is used to introduce nitro groups in the given substrate. It is an electrophilic substitution type of reaction.
H2SO4 is known as sulphuric acid. It is a mineral acid that is odorless, colorless and viscous liquid soluble in water. It is most popularly known as the king of chemicals. It is one of the strongest acid and oxidizing agents.
Alkyl halides undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction. The weak nucleophile is replaced by a strong nucleophile.
Complete step by step answer:
A.Nitrating mixture is used to carry out nitration of the given substrate. It is an electrophilic substitution reaction. In this reaction, the electrophile NO2+ is the incoming electrophile. The halogen chlorine present on the benzene is an electron releasing group. It increases the electron density on the ortho and para position. Hence the incoming electrophile is directed towards the ortho and para position. So the reaction is as follows-
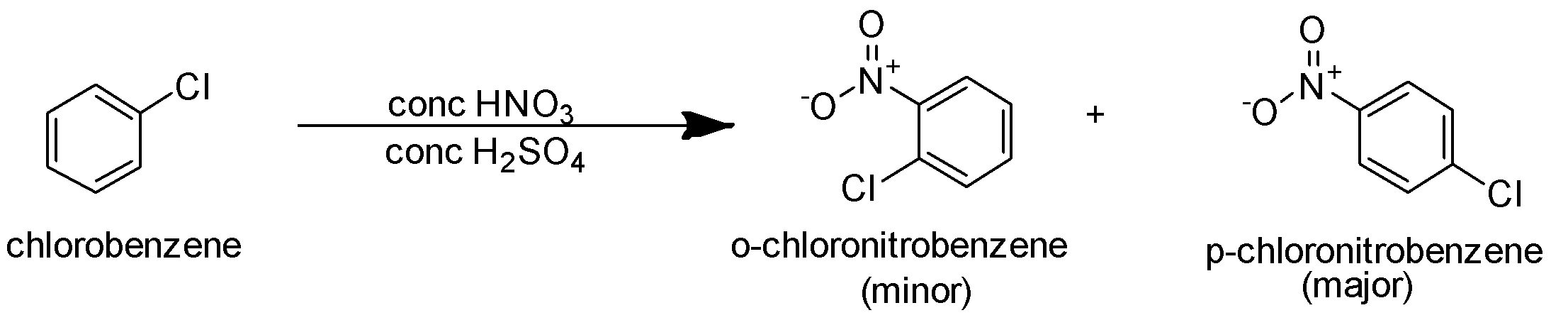
In this reaction p-chloronitrobenzene is the major product.
B.When chlorobenzene is treated with sulphuric acid, sulphonation reaction takes place. It is an electrophilic substitution reaction. The electrophile formed in this case is the sulfonyl group SO3H .Since chlorine present on chlorobenzene is an electron releasing group it increases electron density at ortho and para position. So the incoming sulfonyl group replaces the hydrogen of the aromatic ring present at the ortho and para position. The reaction is as follows-
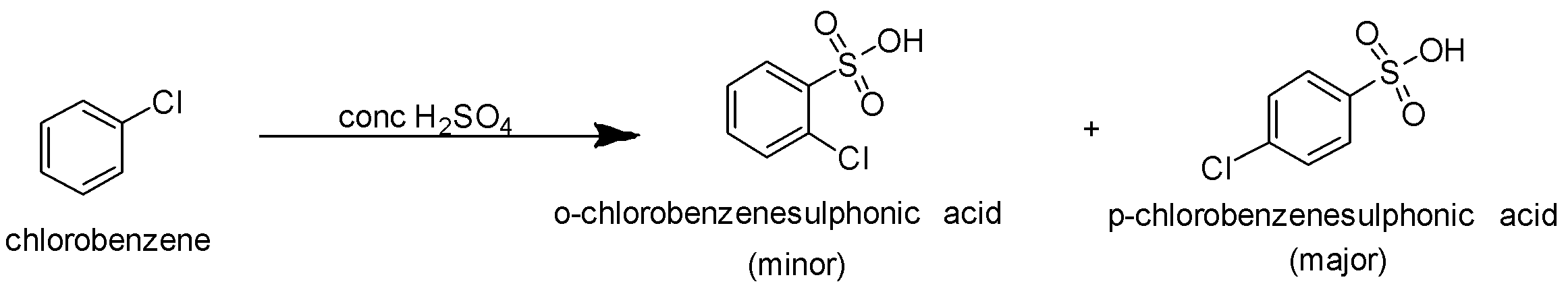
p-chlorobenzenesulphonic acid is the major product.
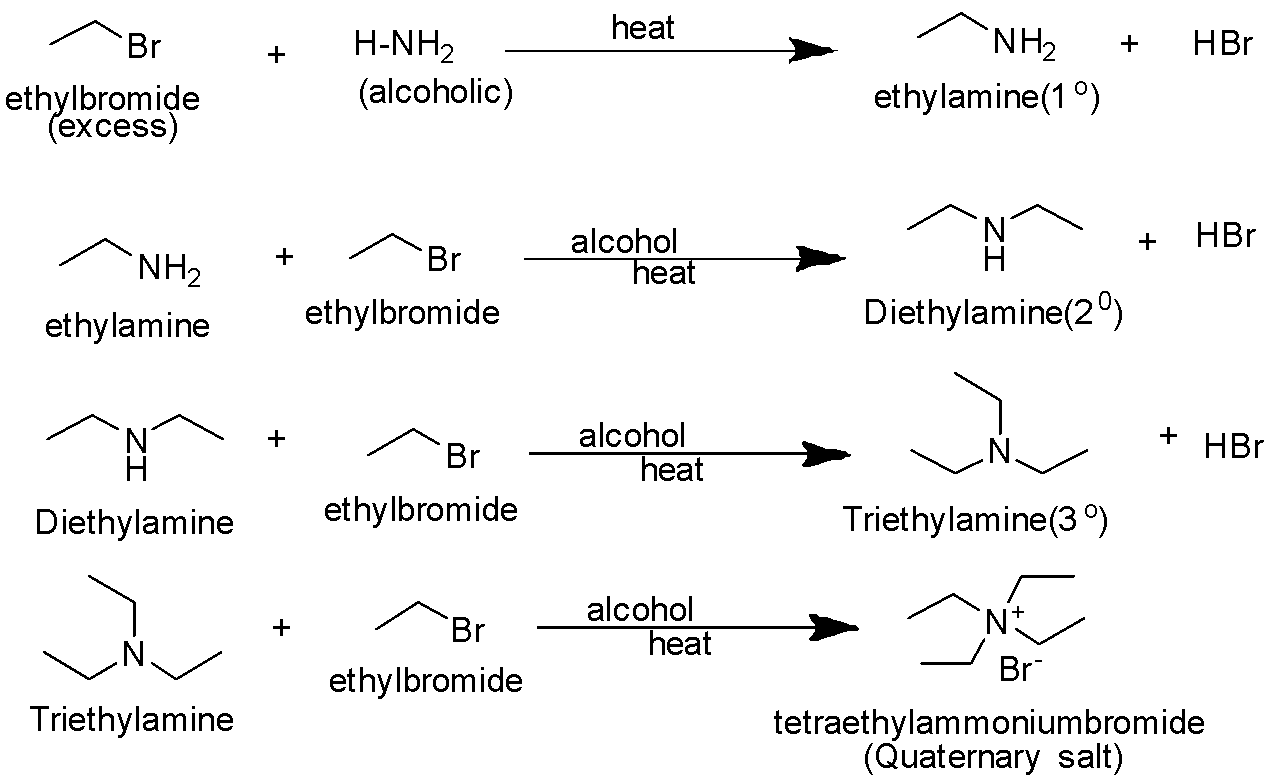
C.When ethyl bromide is treated with alcoholic NH3 , a primary amine is formed. The reaction is as follows-

In this reaction, NH2− is the nucleophile.
When excess of halo alkane is taken reaction proceeds further to finally give quaternary ammonium salt. The primary amine obtained behaves as a nucleophile and can further react with alkyl halide or halo alkane to give secondary and tertiary amines and finally quaternary ammonium salt. This reaction is called Hofmann ammonolysis of alkyl halides.
The reaction proceeds as follows-
Note: 1.Both nitric and sulphuric acids are strong oxidizing agents. The halogen when present on the aromatic ring is an electron releasing group. Though benzene has double bonds it never shows additional reactions like alkenes or alkynes.
2.Remember halogens have negative inductive effect and positive resonance effect. At first we may think that being electronegative they must be electron withdrawing. But this is not the case. Their positive resonance effect is stronger than negative inductive effect. They donate lone pairs of electrons by resonance. Hence they are electron releasing groups and ortho-para directing.
3.The reaction of ammonia on ethyl bromide does not usually stop at the first stage. It continues till the quaternary ammonium salt is formed. Ammonia is a colorless gas, has a pungent odor and is highly soluble in water, alcohols and ether.
