Question
Question: (a) What is meant by ‘ore’ and ‘slag’? (b) Name two metals that occur partly in the native or free...
(a) What is meant by ‘ore’ and ‘slag’?
(b) Name two metals that occur partly in the native or free state.
(c) Name the processes involved in the concentration of ore in metallurgy.
Solution
Metallurgy is a branch of Material science and engineering that involves extraction of Metals in their pure state from some or other combinations with which these are present. This extraction involves several chemical principles. It is important that the process should be economically viable and chemically feasible. Metallurgy is a scientific process.
Complete answer:
(a) Ore- Ores are naturally occurring rocks. Metals are obtained from minerals that are naturally occurring substances present in the earth crust. However all minerals are not suitable for obtaining metals. Thus ores are those minerals that are used to obtain pure metals.
Some popular examples of metals and their ores are-
| Metal | Ores |
|---|---|
| 1.Iron | Haematite Limonite Magnetite Siderite Iron pyrite |
| 2.Copper | Cuprite Copper glance Copper pyritesMalachite |
| 3.Zinc | Zinc blende Zincite Calamine |
| 4.Aluminum | Bauxite Corundum Feldspar Cryolite Alunite Kaolin |
| 5.Silver | Ruby silver Horn silver |
| 6.Mercury | Cinnabar |
Slag-Slag is the by-product obtained after the separation of metal from ore has taken place. It is mostly a mixture of Metal oxides and silicon dioxides. It prevents oxidation of metal by floating on its surface. Although it contains several undesirable impurities necessary for protection of metal and shows glassy appearance.
(b)Examples of 2 metals that exists in both free and combined states are- Silver (Ag) and Copper (Cu).Silver exists in free as well as combined form as AgCl,Ag2O while copper also exists in free as well as combined form as CuO,Cu2O etc.
(c)There are 3 steps in extraction of metals-concentration of ores, obtaining metal from ore and purification of metal.
Concentration- Concentration is the method of removal of impurities (gangue) like clay, sand, dust etc. from the ore. It is the process of removal of unwanted material. It is also called dressing or benefaction.
The several processes involved in concentration of ore are as under-
(1)Hydraulic Washing- This process is based on the difference in the gravity of gangue and ore particles. Here we pass a stream of water through the ore and lighter gangue particles are removed and heavier particles stay there. It is a type of gravity separation method.
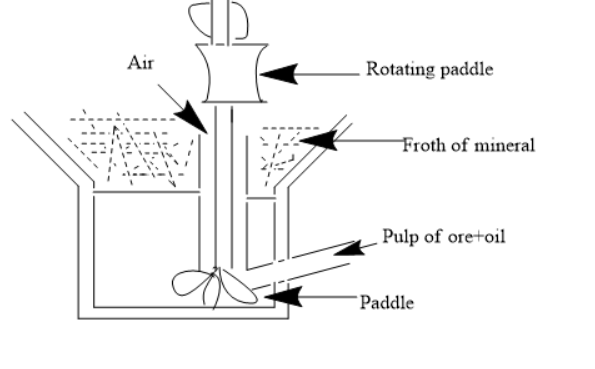
(2)Froth flotation Method- This method is useful to remove gangue from sulphide ores. A suspension is made of powdered ore. Collectors (like pine oil) and stabilizers (like aniline) are added to it. Collectors are for non-wettability of mineral particles while the stabilizers stabilize the froth. There is a rotating paddle which agitates the suspension and we obtain the froth. The oil wets the mineral particles and water wets the gangue. So overall the process is based on the difference in adherence of particles. The froth is then dried to obtain ore particles.
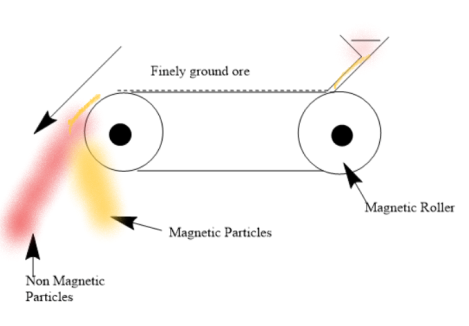
(3)Magnetic Separation- This process involves the use of Magnetic properties of either the gangue or mineral particles. The ore is firstly ground and then passed on to conveyor belt passing over a magnetic roller. The gangue falls off the belt while the Magnetic ore will stay. For example- Iron ores remain on the belt while the impurities fall off.
(4)Leaching- Leaching is the process used when ore is soluble in a certain solvent. Common example is Leaching of Alumina from bauxite. In this case the ore is soluble in concentrated solution of sodium hydroxide NaOH and from this solution we obtain the dissolved metal Aluminium.
Note:
Metallurgy is thus an integral part of human civilization and chemical industries for a very long period of time. It is broadly classified as Electro metallurgy, pyro metallurgy, Hydro metallurgy and bio metallurgy. They form the backbone of the Aircraft, Automobile, coins, jewellery industry.
