Question
Question: A. What is cross pollination? Write only the names of different types of cross pollination. B. Des...
A. What is cross pollination? Write only the names of different types of cross pollination.
B. Describe the germination of pollen grains with the help of a diagram.
Solution
Pollination is the process of transfer of pollen grains (microscopic structures having the male gamete) from the anther (male reproductive structure) to the stigma (female reproductive structure) of the flower. This is a pre-fertilization event in the sexual reproduction observed in angiosperms, which are the flowering plants. Pollination can be of two types - Self and cross pollination. For fertilization to occur pollination should be completed successfully between compatible pollen and stigma.
Complete answer:
To solve this question, we have divided it into two parts A and B.
Solution of Part A,
In this part, the question is on cross pollination.
Cross pollination is a type of pollination taking place between two different flowers of the same or different plants of the same species (generally).
More specifically, in cross pollination the pollen grain from the anther of one flower is transported to the stigma of another flower and the two flowers involved can be located on the same plant or may be present on different plants of the same species in order to ensure compatibility of gametes during fertilization.
Cross pollination can occur only with the help of a vector which can transport the pollen grain from one flower to another flower. So based on the agency or vector involved cross pollination can be of many types as follows:
Hydrophily - Pollination caused by water
Zoophily - Pollination caused by animals
Anemophily - Pollination caused by wind
Entomophily - Pollination caused by insects
Ornithophily - Pollination caused by birds
Solution of Part B-
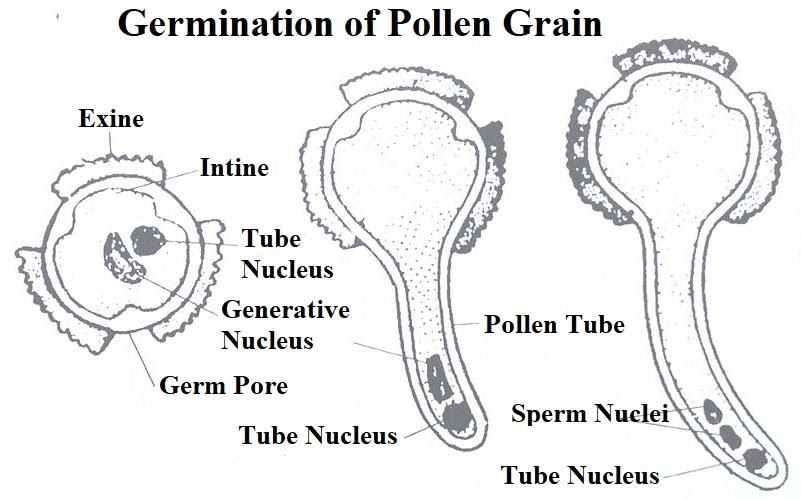
Now, this part asks about the germination of pollen grain. So, basically, we need to explain the sequence of events that takes place after the pollen has landed over the stigma.
Once the pollen grains reach a compatible stigma, they germinate to form a pollen tube through which the male gamete travels towards the ovary of the flower to fuse with the female gamete and lead to syngamy or fertilization.
In flowering plants, the ovule is contained in a hollow organ called the pistil, and pollen is deposited on the surface of the pistil, the stigma. The pollen grains begin to germinate with the absorption of water and nutrients, and the pollen grains form a small pollen tube that passes through the shaft to reach the ovary. Tubular cells grow and leave the pollen grains through a hole in the stigma and form pollen tubes. The tube nucleus reaches towards the growing end of the pollen tube. Germ cells then split into two male gametes and soon enter the pollen tube.
Note:
Pollination is a crucial event in the survival of many flowering plants and a successful pollination can lead to fertilization, seed formation, fruiting and seed dispersal in order to ensure the distribution of plant species. Cross pollination caused by insects is an example of the mutualistic relationship between the pollinator and the plant. Moreover, it ensures the genetic variability in a plant species. The germinated pollen grain with its two sperm cells is the mature male microgametophyte of these plants.
