Question
Question: (a) What are isomers? Write the structures of two isomers of butane (\({{C}_{4}}{{H}_{10}}\)). (b)...
(a) What are isomers? Write the structures of two isomers of butane (C4H10).
(b) write the name and chemical equation for the reaction that takes place when 5 solution of alkaline KMnO4 is added drop by drop to warm ethanol.
(c) Name the product formed when ethanol is heated at 443K with excess conc. H2SO4 and the state the role of conc.H2SO4 in the reaction.
Solution
Isomers are those compounds which have similar molecular formula but difference lies in their physical properties. When alkaline KMnO4 is added to ethanol, it forms the compound which consists of the −COOH as the functional group and when ethanol is heated with excess conc.H2SO4, it results in the formation of an unsaturated compound. Now you can easily answer the statements accordingly.
Complete Solution :
We will discuss the statements one by one as;
(a) Isomers are the organic compounds which have the same molecular formula but different properties i.e. structure and the arrangement of the atoms in the space and the phenomenon is known as the isomerism.
The two structural isomers of butane have the same formula as C4H10 are;
1. n-butane
CH3−CH2−CH2−CH3
2. Iso-butane
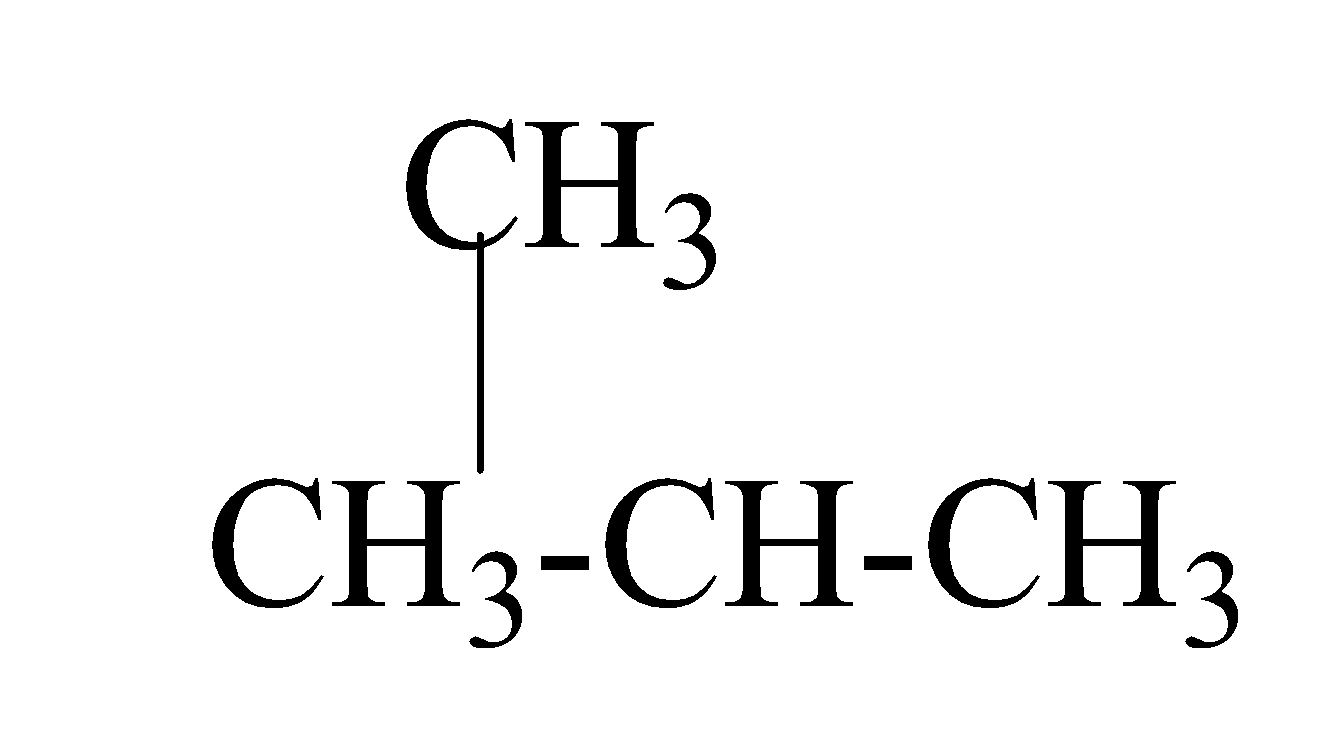
(b) When alkaline KMnO4 is added drop by drop to warm ethanol , it undergoes reduction and results in the formation of acid i.e ethanoic acid. The reaction occurs as;
CH3CH2OH+alk. KMnO4→CH3COOH
(c) When ethanol is heated at 443K with excess conc.H2SO4, it results in the formation of alkene along with the water. The reaction occurs as;
C2H5OHH2SO4443KCH2=CH2+H2O
Thus, conc.H2SO4 acts as a dehydrating agent and removes the water from alcohol and forms alkene.
Note: Isomerism are of two types:
1. Structural isomerism :- In this type of isomerism, the molecules have the same molecular formula but differ in the arrangement of the atoms within the molecule. Example : position isomerism, chain isomerism etc.
2. stereoisomerism:- In this type of isomerism, the molecules have the same molecular formula but differ in the arrangement of the atoms in the space. Example: geometrical isomerism, optical isomerism etc.
